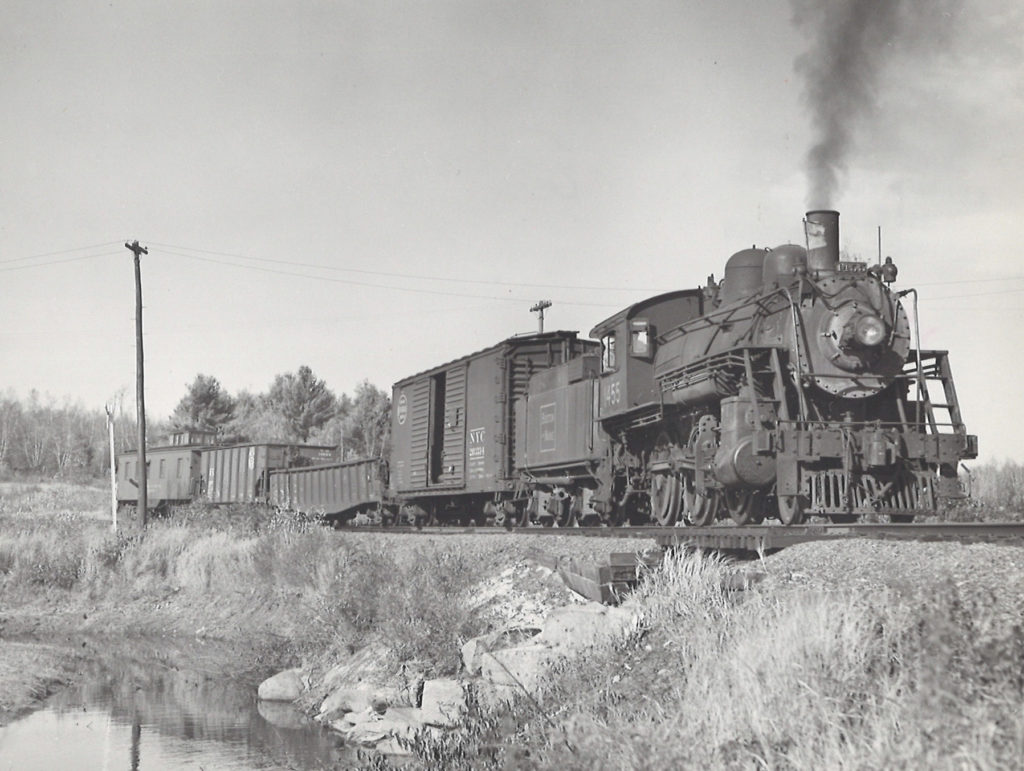

Our sister magazine, Classic Trains, named Boston & Maine the railroad of the month for October 2019. Please enjoy this photo gallery of images from the David P. Morgan Library archives at Kalmbach Media that include B&M steam-powered freight trains through time. […]
Read More…
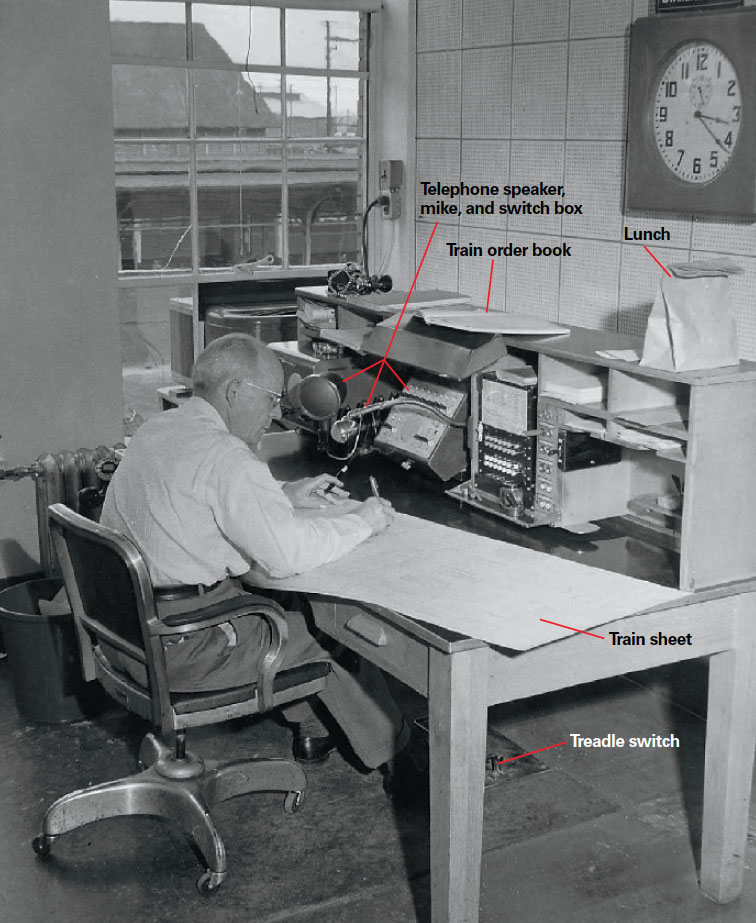

A train dispatcher supervises the movement of trains over a designated portion of a railroad and also supervises the other employees involved in that movement. The dispatcher’s first responsibility is safety, to see that each train gets over the road without trying to occupy the same piece of track at the same time as any […]
Read More…

Model Railroader magazine remains the leading source of information for our great hobby. You can get access to all of the more than 1,000 issues of Model Railroader from January 1934 to the present day by signing up for the exclusive online archive. Check out this classic story from the April 1988 issue. […]
Read More…
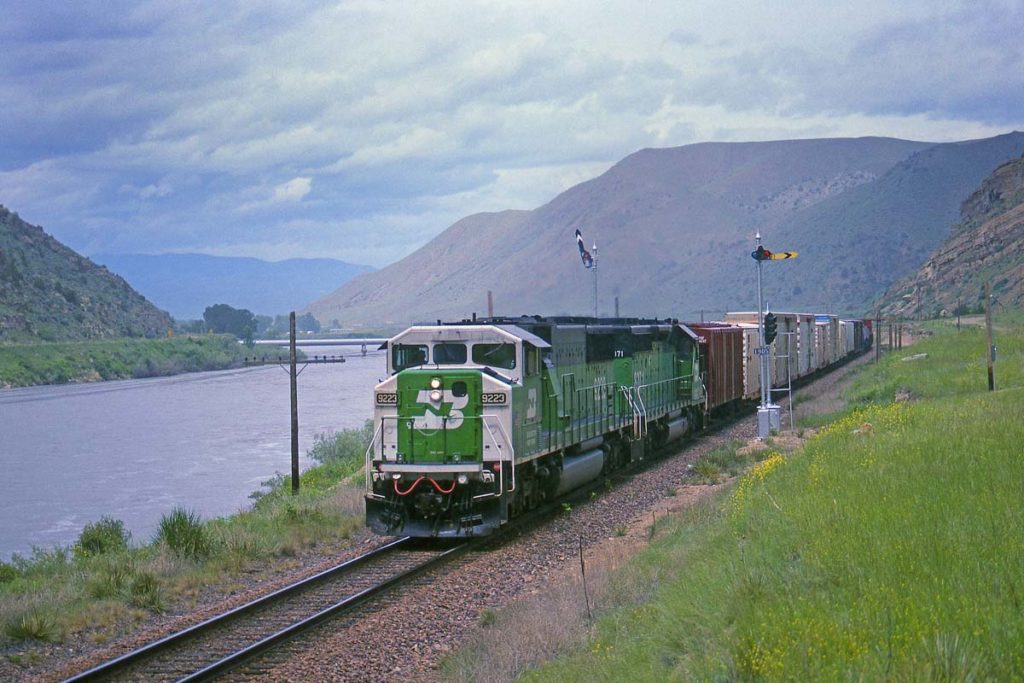

On June 10, 1993, a Burlington Northern SD60M and SD40-2 take an eastbound freight along the Missouri River and into Lombard Canyon just east of Toston, Mont. Tom Danneman Learn about Trains Art Director Tom Danneman’s favorite Burlington Northern Railroad Company diesel locomotives, presented in no particular order. The story of Burlington Northern has been […]
Read More…
The Cold hard tracks Crystal Lake was once used for harvesting ice. Blocks of ice were cut from the lake in winter, then stored in warehouses along the shore. The ice was shipped in refrigerator cars to Chicago via the “Ice Track,” a 2-mile branch that ran from the C&NW main line through the west […]
Read More…

Not everyone has a fabulous railroad library to work from, but the library at the Model Railroader offices didn’t get me as far as you’d think. Following is a short list of places I’ve found amazing stuff when looking for research: • Most railroads have a historical society, so it’s good to have an up-to-date […]
Read More…
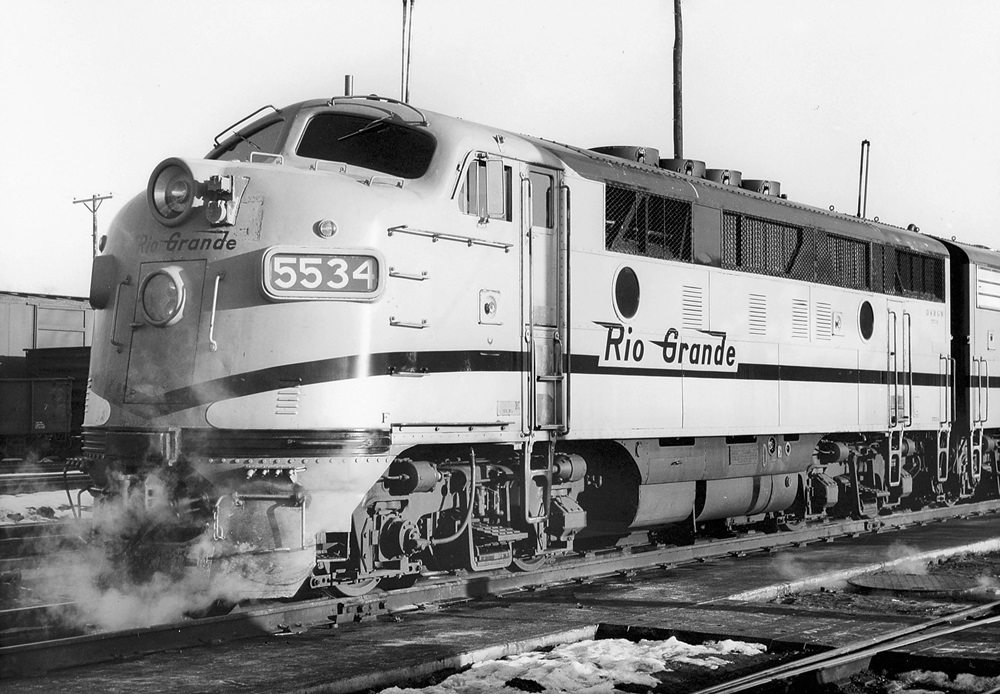

Classic Trains editors are celebrating the heritage, history, and lore of famed (and infamous) railroads. In December 2019, we celebrate the Denver & Rio Grande Western. Please enjoy a collection of locomotive images located in the David P. Morgan Library archives at Kalmbach Media that include the Rio Grande’s iconic locomotives and classic scenic […]
Read More…
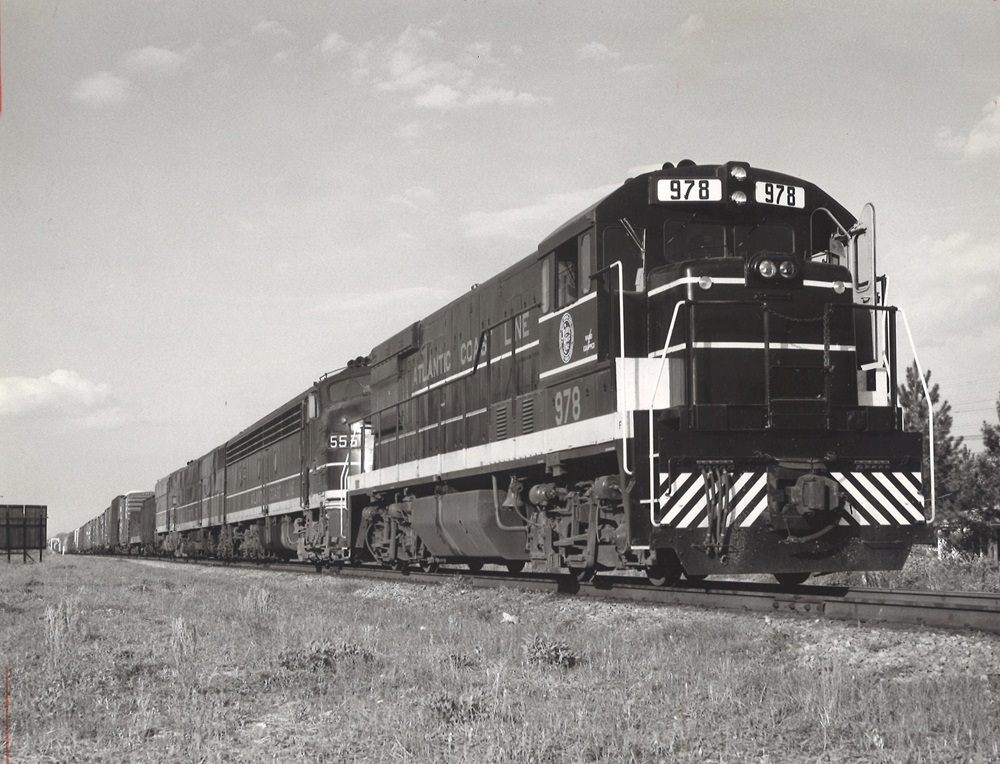

All this month — November 2019 — Classic Trains editors are celebrating the heritage, history, and images of the Atlantic Coast Line Railroad. Please enjoy this photo gallery of images from the David P. Morgan Library archives at Kalmbach Media that include ACL diesel- and steam-powered freight trains through time. […]
Read More…
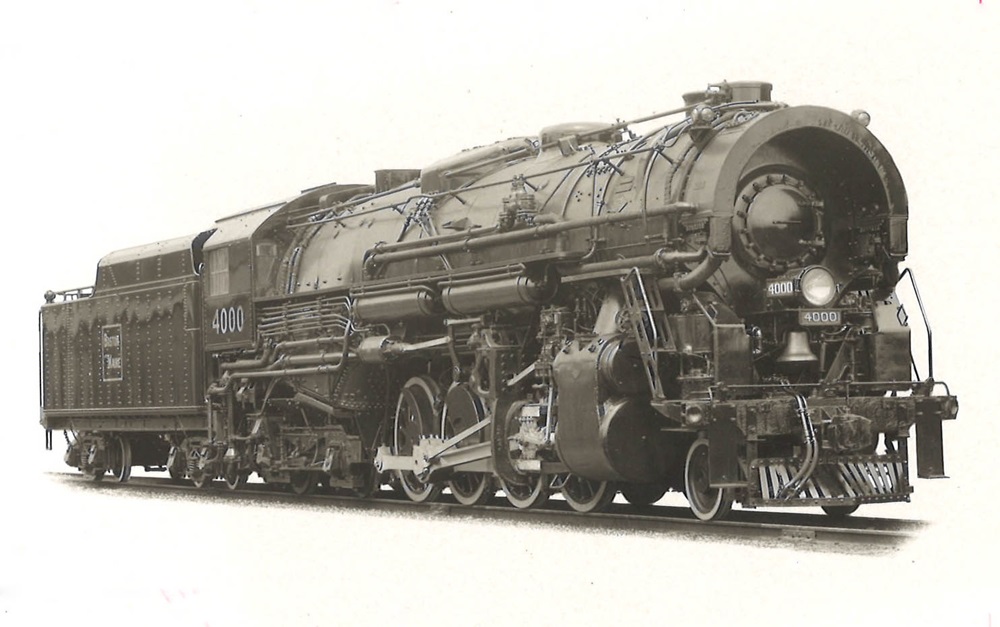
Starting in October 2019, Classic Trains editors will celebrate the heritage, history, and lore of famed (and infamous) railroads. We start this series with the beloved Boston & Maine. Please enjoy a collection of images located in the David P. Morgan Library archives at Kalmbach Media that include B&M’s iconic locomotives and scarce builder’s photos. […]
Read More…
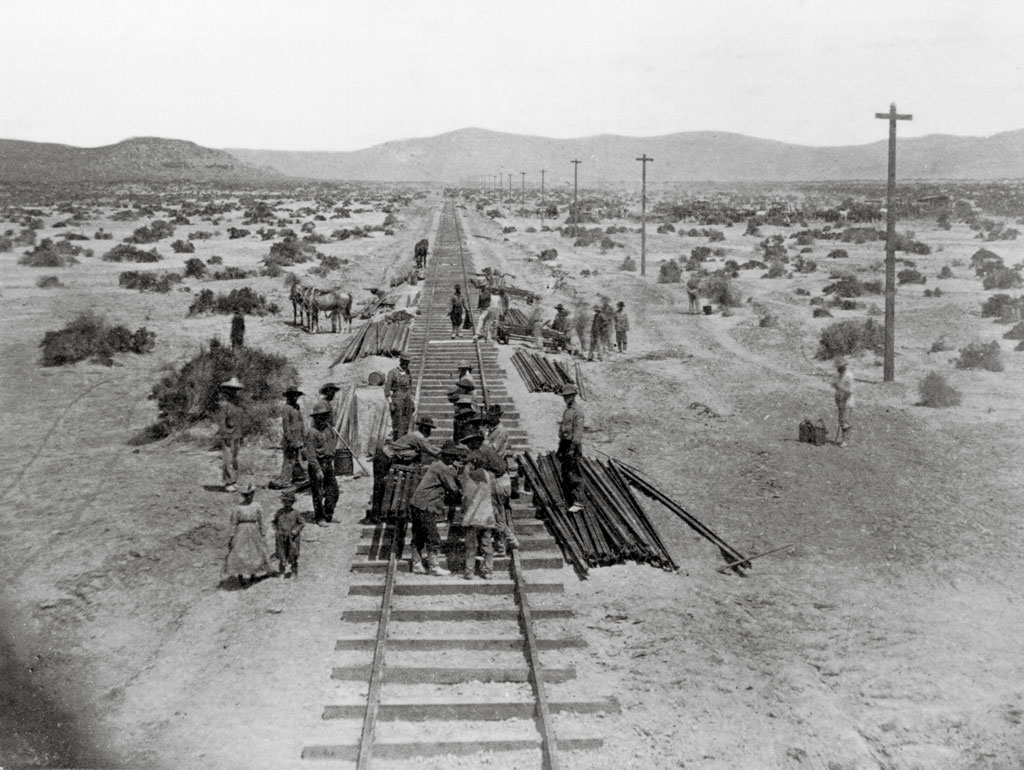

Chinese workers load rail onto a tracklaying car from the piles left by the morning’s supply train. Sixteen rails, a keg of spikes, a keg of nuts and bolts, and 32 splice bars, along with the crew made the load. Horses to pull the car stand ready. The location is Granite Point, Nev., in late […]
Read More…
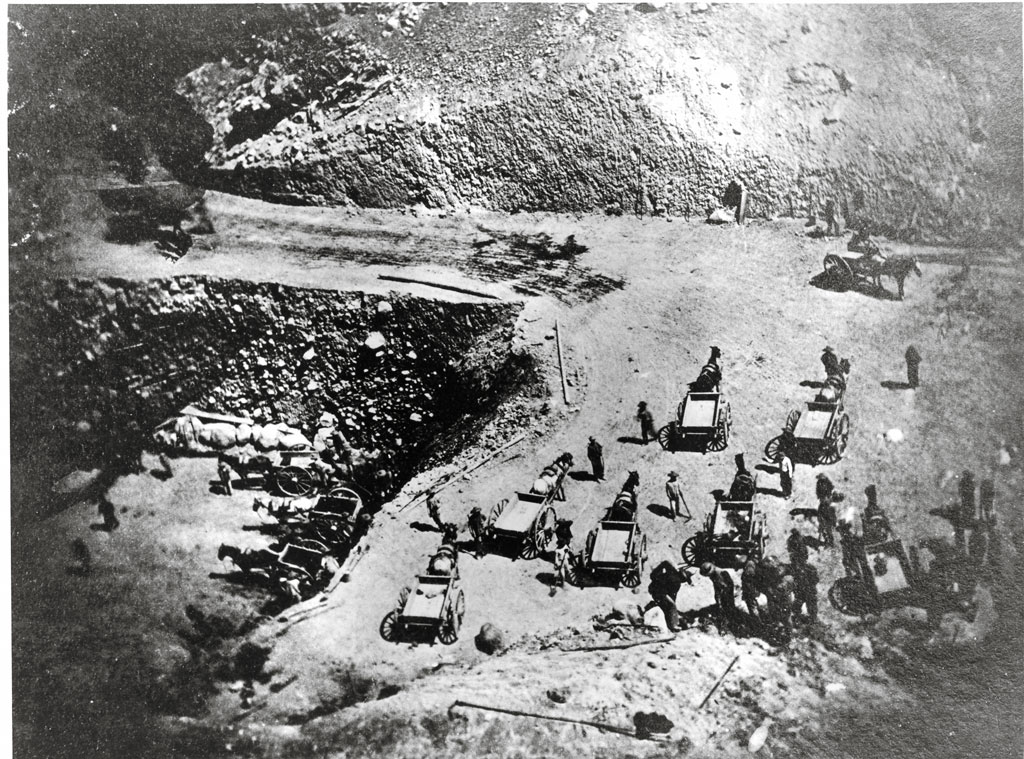

Grading on the Central Pacific was done by hand, relying primarily on Chinese using picks, shovels, and horse-drawn dump carts, though black powder was freely used to break hard soil and move rocks aside. This scene is the 170-foot deep excavation at Prospect Hill, Calif. It dates from summer 1866, when more than a thousand […]
Read More…
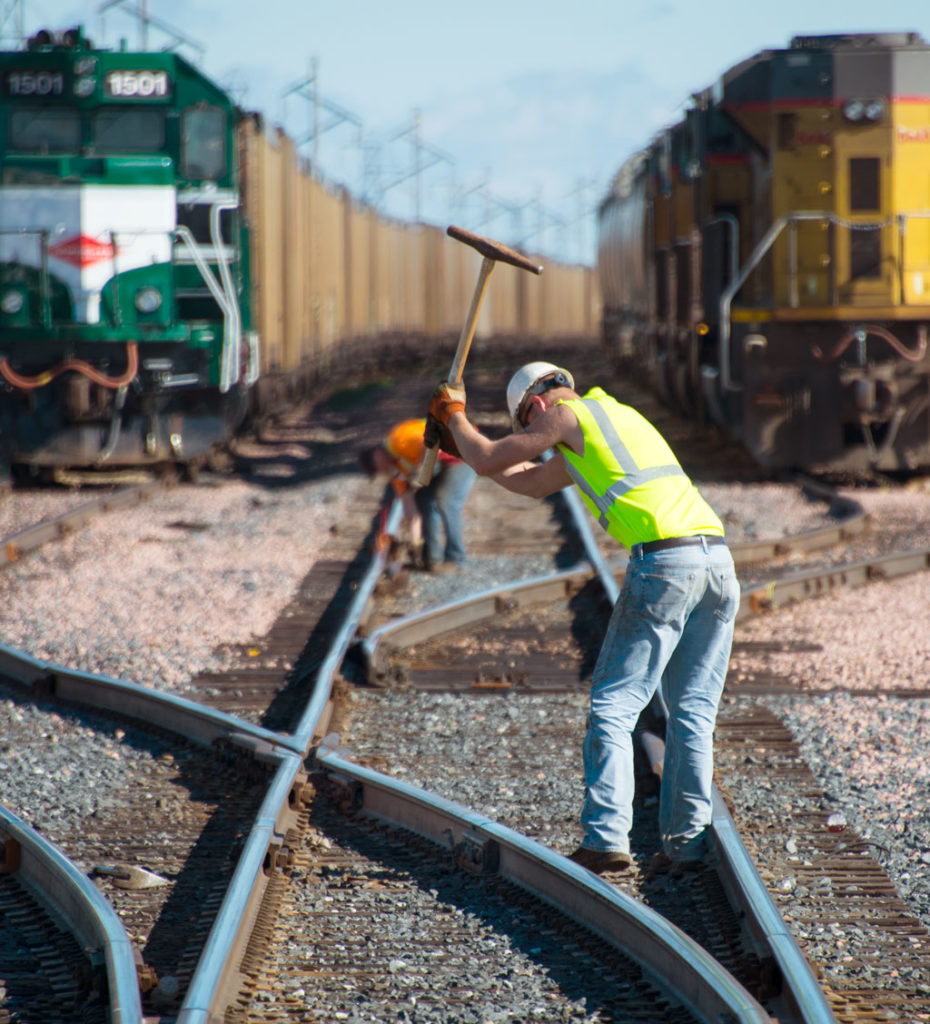

A track worker hammers in spikes on a turnout. Steve Smedley Rusty track spikes near Canadian Pacific tracks at Brookfield, Wis, in 2012. Karl Riek The Golden Spike of the first transcontinental railroad was but one of millions in the nearly 2,000-mile route between Sacramento, Calif., and Omaha, Neb. Spikes date back to the first […]
Read More…











