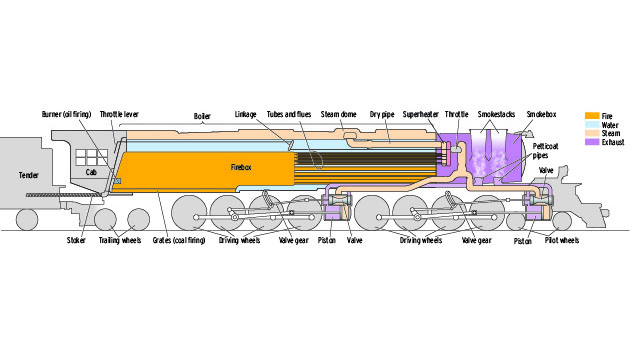
Where does the fire burn? Where does the water boil? Where does it travel? What are all those pipes about? Our simplified drawing of how a Big Boy works shows how this king of the rails made and used steam to pull long freight trains up to 70 mph in Wyoming and Utah from 1941 […]
Read More…
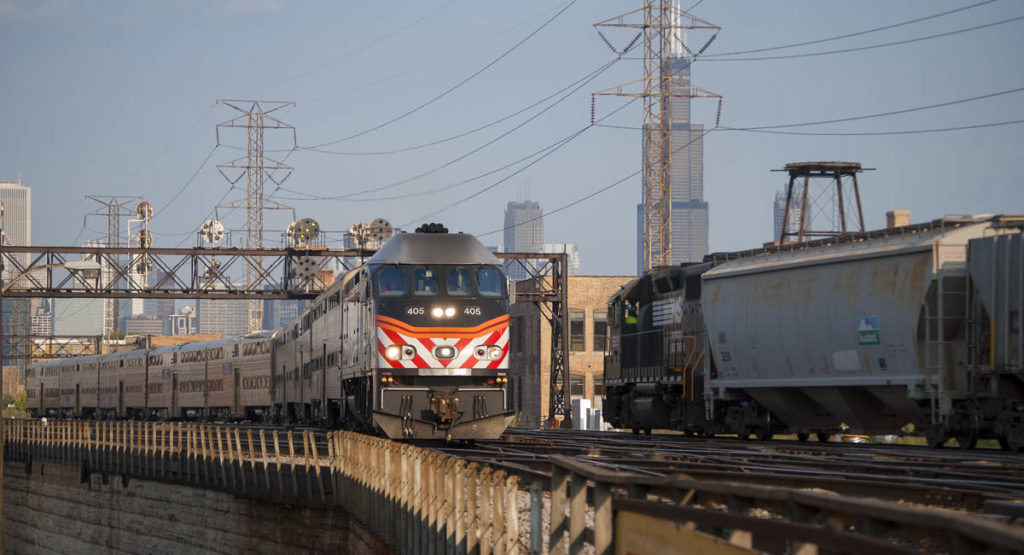

Metra commuter and Norfolk Southern freight trains meet at tower A2 northwest of Union Station. Steve Sweeney Trains tracks the evolution of positive train control technology from the 1980s to present! August 1985 – Burlington Northern executives approve testing a PTC prototype system, ARES, in Minnesota’s Iron Range. May 1, 2007 – U.S. Rep. James […]
Read More…

Cummins QSK95 test locomotive No. 1919 uses Selective Catalytic Reduction aftertreatment of its exhaust. The system is located in the wing overhang; a urea and water solution tank is inside the forward portion of the fuel tank below the forward air reservoir. Chris Guss With Environmental Protection Agency Tier 4 emission regulations in effect for […]
Read More…
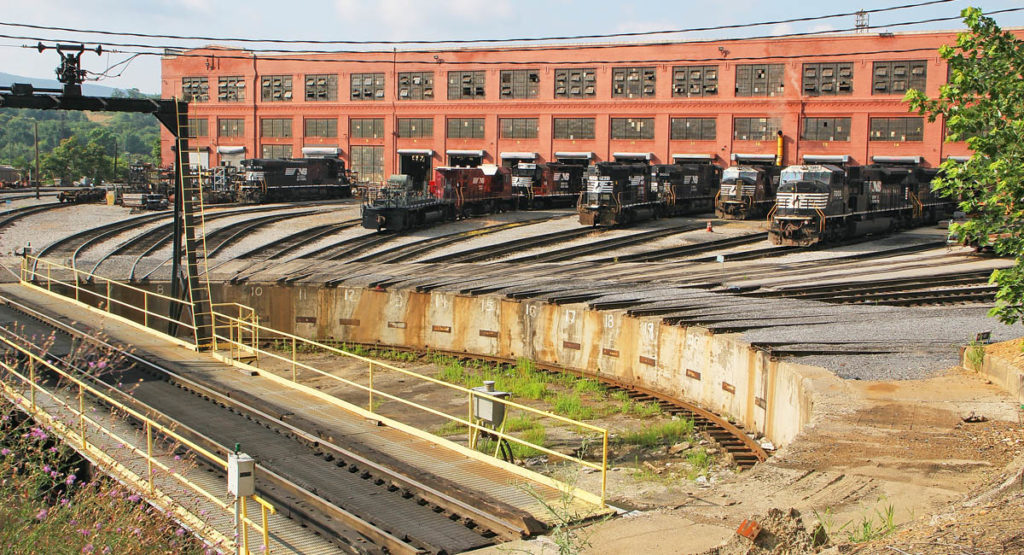

Home for the heaviest rebuild, repair, and repaint work on the Norfolk Southern system is the sprawling former Pennsylvania Railroad Juniata Shops in Altoona, Pa. The backshop is the heart of this operation in the Keystone State. Alex Mayes Diesel locomotives are amazing. They are built to withstand the rigors of service, running 24 hours […]
Read More…
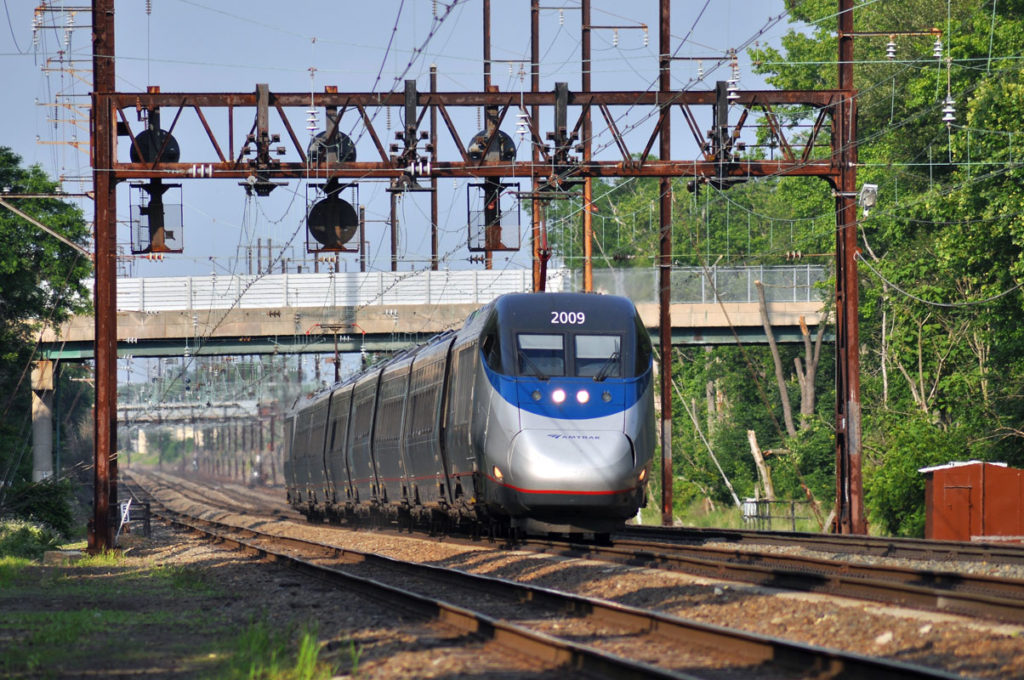

A southbound ‘Acela’ races across a stretch of positive train control trackage on Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor at Perryville, Md., on June 5, 2011. Michael T. Burkhart This story first appeared in the October 2011 issue of Trains Magazine. The Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System highlighted here was not active at the time of the of […]
Read More…

Confidential Close Call reporting basics A New Jersey Transit train zips northward from Atlantic City to New York’s Penn Station on Jan. 23, 2010. If the crew were to err, they could report the close call and be part of a bigger program to improve safety, rather than be punished. Dennis A. Livesay photograph Confidential […]
Read More…

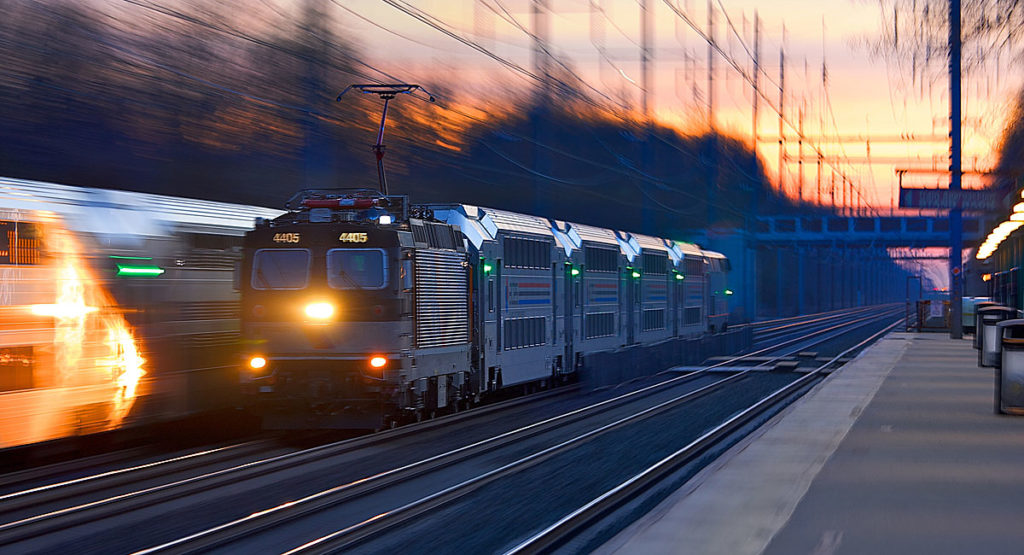
Positive Train Control Tick, tock. U.S. railroads have collectively spent decades and billions of dollars on positive train control research. Tick. Public outcry after a 2008 commuter crash that killed 25 people — a crash that a Federal safety panel says PTC could have prevented — pushed Congress to act. Tock. With a Congressional deadline […]
Read More…
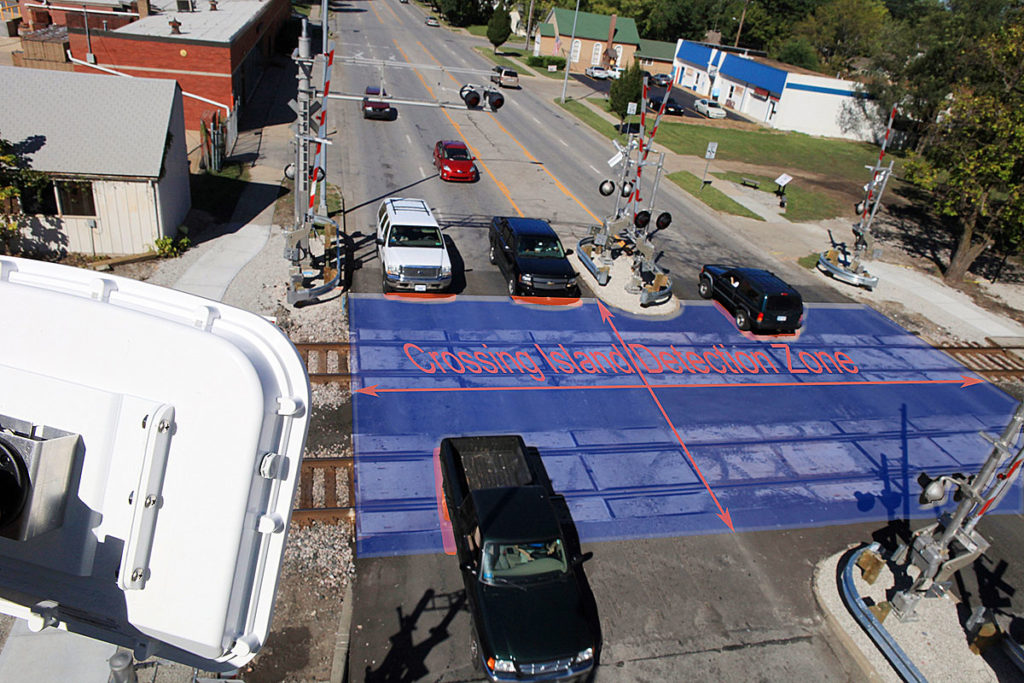

Intelligent Grade Crossings will warn motorists and trains that approach is imminent. Federal Railroad Administration Train crews and motorists may have the ability to “see” one another earlier than ever thanks to “Intelligent Grade Crossings” currently under development through the Federal Railroad Administration’s Research and Development Office. Since the dawn of railroading, one of the […]
Read More…

Northbound CSX Transportation aggregates train K944 is seen meeting intermodal train Q145 at Opelika, Ala., in 2010. Class I railroads use different kinds of schedules to keep their networks fluid and profitable, even on single-track lines. Frank Orona What time will the train depart? When will it arrive? While most people associate schedules with passenger […]
Read More…
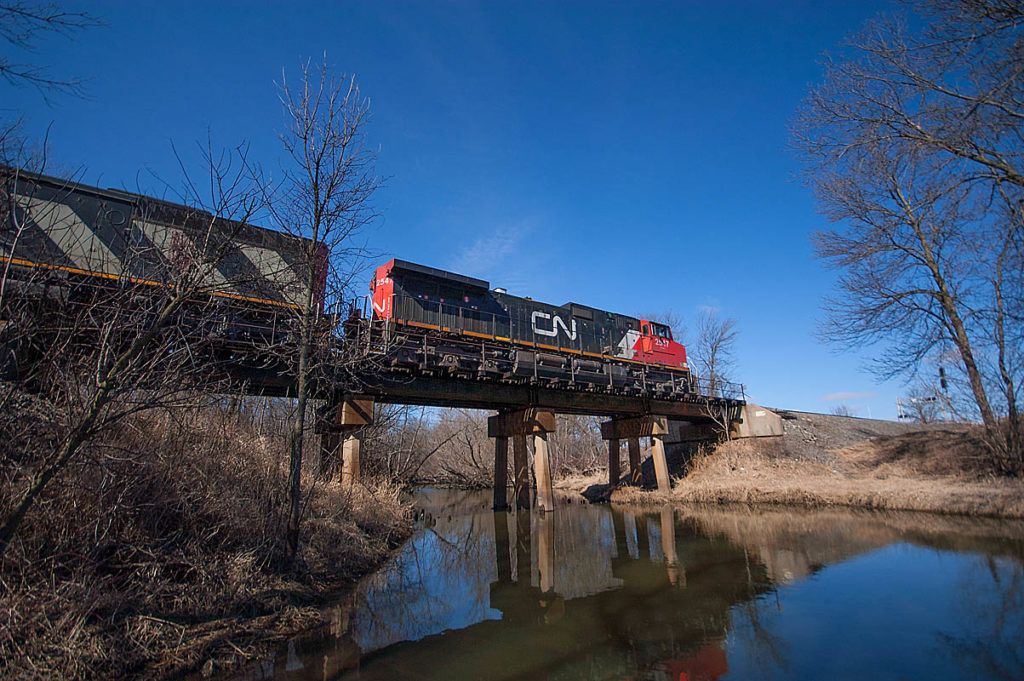

A Canadian National train heads north through Wisconsin over a bridge in 2015. Regardless of the location or railroad, bridges pose problems for track. Steve Sweeney Track can sag, bounce, and shift a bit, within reason. It flexes under the weight of heavy freight trains, but bridge ends don’t. And that’s a problem. When most […]
Read More…
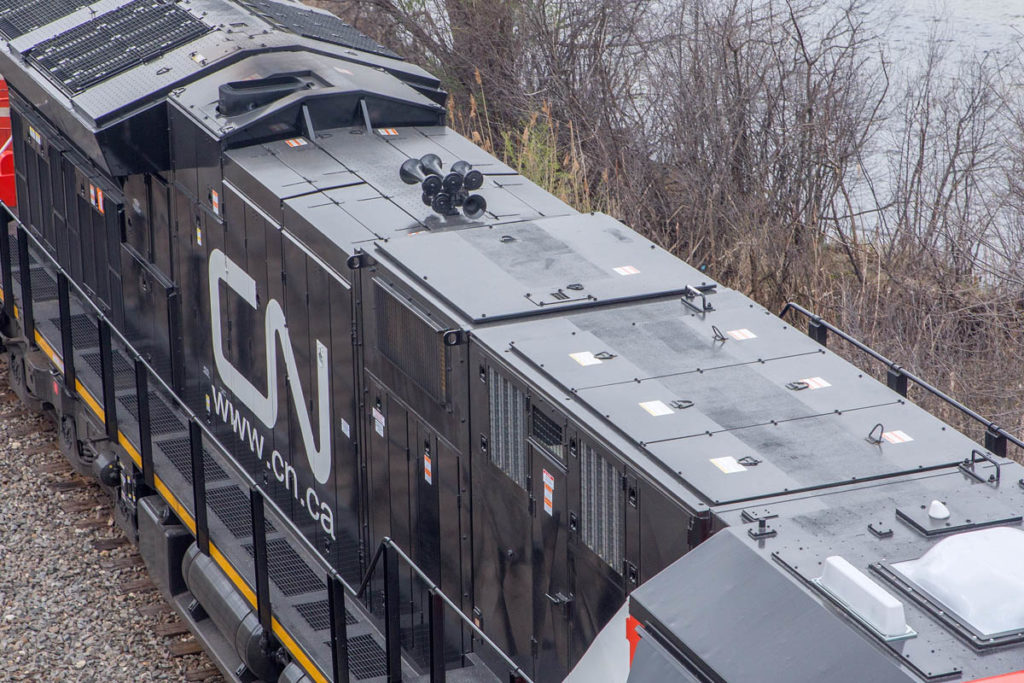

Horns are typically placed near the middle of the locomotive to minimize noise to the crew. New Canadian National ET44AC No. 3062 shows off its Nathan K5HLR2. Chris Guss A horn is one of the many safety appliances installed on a locomotive and is used to warn both the general public and railroad employees while […]
Read More…
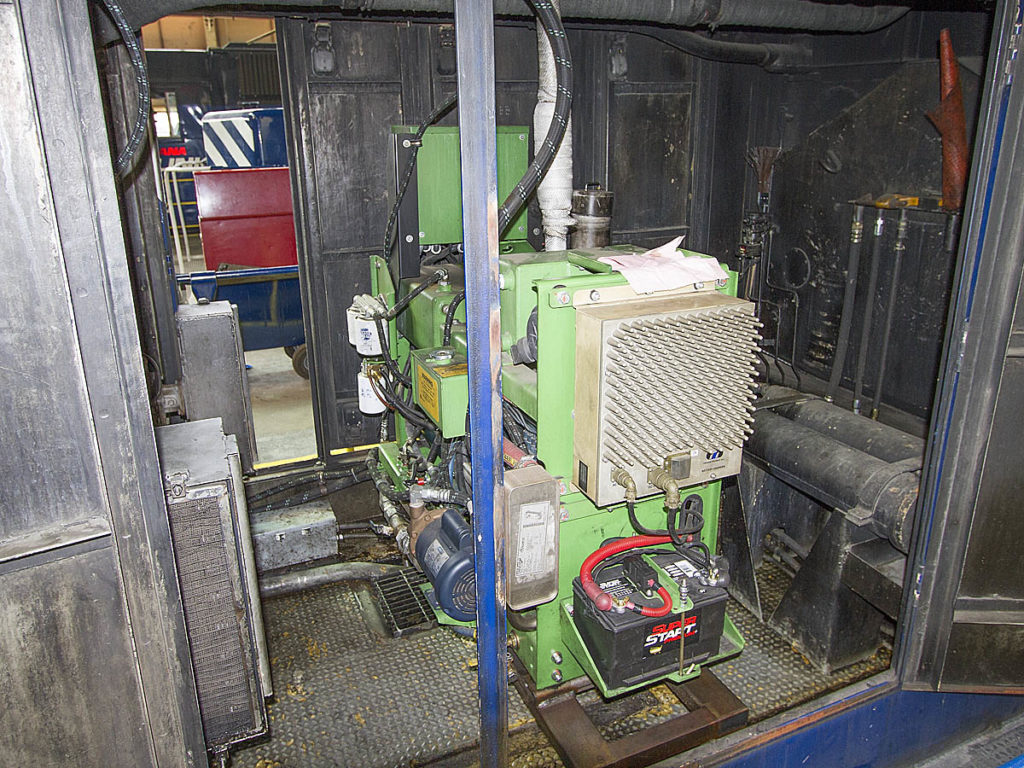

Auxiliary power units can be installed in a variety of locations, but are typically installed in the rear of the long hood, like this one on a Montana Rail Link locomotive. Tom Danneman Idling locomotives have been a regular part of the railroad industry since the switch from steam to diesel in the 1950s. Locomotives […]
Read More…












