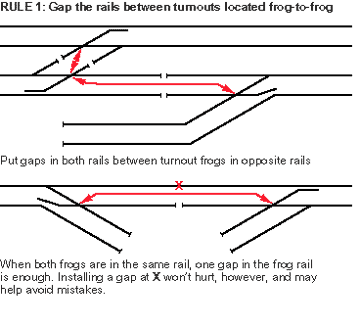
How to wire power-routing turnouts: While it may initially seem difficult, basic two-rail wiring for power-routing turnouts is easy if you understand and apply just two simple rules. The diagrams below demonstrate these crucial wiring principles. Rule 1: Gap the rails between turnouts located frog-to-frog. Place gaps in both rails, between turnout frogs in opposite […]
Read More…
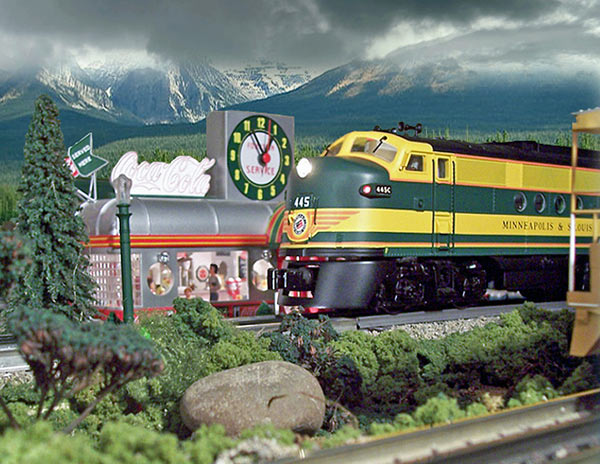

Paul Helgeson has less than 100 square feet dedicated to his layout, but the variety of scenes is astonishing. Here we offer some additional photographs showing more of his spectacular modeling. Click on each photo to see a larger image. […]
Read More…
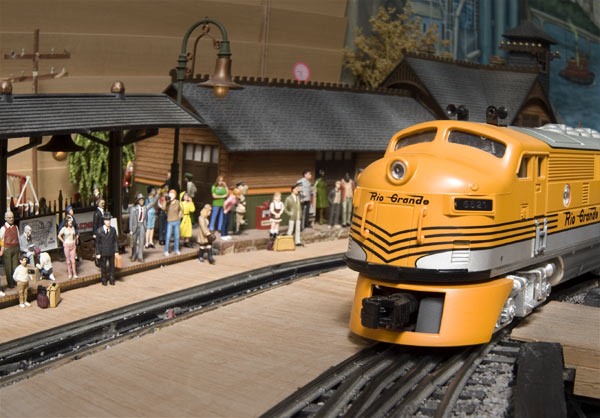

Sometimes we have more photos than we can possibly fit in the allotted pages for a layout article. After choosing the ones we considered to best illustrate the story of Wayne’s layout, we thought we’d share some of the “outtakes” with our subscribers for even more sights on this fabulous railroad. Click on each photo […]
Read More…

A messy work area is not only unsightly, it is unsafe. A shop floor needs to be kept clear of dust and debris. Losing your footing can result in a sprained ankle, not to mention hitting your head on your workbench. Sweeping up at the end of your work session is all that is needed […]
Read More…

Rail comes in many different sizes and materials. Here’s a little background information to help you chose the one that’s right for you. Rail sizes The size of model-train rail in any scale is referred to by “code.” For instance, in large-scale railroading we commonly use code-332, code-250, or code-215 rail, although code 197 is […]
Read More…

Annual refers to a plant that lives for only one season and must be replanted each year. Ballast is the medium, usually gravel of some sort, that provides a firm underlayment for track, helps to hold it in place, and drains water away from the ties. Battery power is another way of operating electrically powered […]
Read More…

Bob Temper • Don’t arrive early. Most garden railroaders tend to work frantically up until the last minute getting their lines ready. Arriving early can be disruptive. • Don’t stay late. Our hosts are exhausted by the end of the day, so please leave by closing time. • Sign the guest book. Owners like to […]
Read More…

Jeff Young Full-size steam locomotives have been in existence for over 200 years, and live-steam models for nearly that long. On that basis, it might be easy to conclude that the hobby of small-scale live steam is one that would not see a lot of new technology. To the contrary, there have been a number […]
Read More…

Download this free trackplan that accompanies our Tuscarora project railroad series. In the June 2006 issue: Determining a trackplan, surveying the land, and defining objectives In the August 2006 issue: Breaking ground and building a stone retaining wall In the October 2006 issue: Building a PVC-based trackbed In the December 2006 issue: Laying track In […]
Read More…
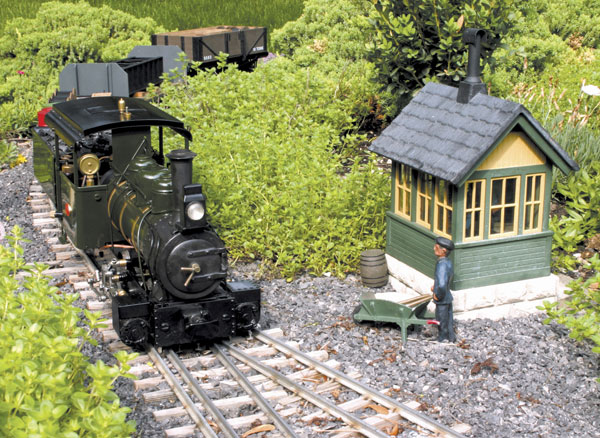

A Roundhouse “Fowler,” fitted with a coal-fired boiler by John Shawe, at work on the author’s garden railway near Toronto. Jeff Young photo When we acquire a small-scale live steamer, it is usually to run on an established garden railway. The selection of your live-steam locomotive was probably influenced by the physical characteristics of the […]
Read More…

The No. 24 was the last locomotive supplied to the two-foot gauge Sandy River & Rangeley Lakes Railroad in Maine. This G scale live steam model was manufactured by Roundhouse Engineering of Doncaster, England. Kenneth Matticks Gas is added through the filler valve in the center of the tank. By watching the pressure gauge and […]
Read More…

Lillian “Curly” Lawrence and the history of live-steam locomotives Lillian “Curly” Lawrence was a British model engineer who lived from 1882 to 1967. He built his first live-steam locomotive at the age of 13 on a used treadle lathe. A curious and reclusive fellow, he wrote live-steam columns for British model-engineering magazines under the pen […]
Read More…











