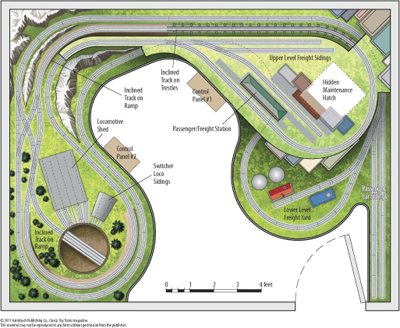
Layout designer: Geoffrey Kumagai Scale: O Layout size: 12 x 16 feet Track type: Atlas O Minimum curve: O-54 Originally appeared in the November 2000 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Second Honorable Mention in Classic Toy Trains magazine’s first layout planning contest: Plans for a 12 x 16-foot room. Click on this link to download […]
Read More…
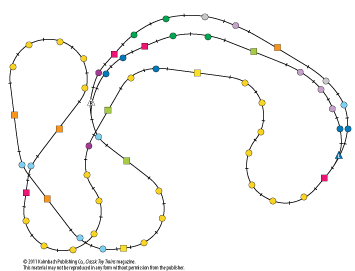
Layout designer: Don Woodwell Scale: O Layout size: 12 x 16 feet Track type: GarGraves Minimum curve: O-42 Originally appeared in the October 2005 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the links below to view PDF’s for Conquering the Canadian Rockies. Track Plan Schematics Parts List […]
Read More…
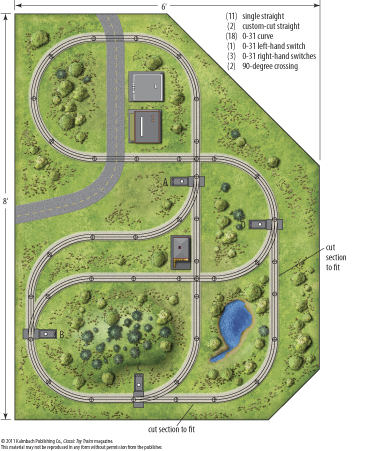
Layout designer: Neil Besougloff Scale: O Layout size: 6 x 8 feet Track type: Lionel O Minimum curve: O-31 Originally appeared in the September 2003 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click here to view a pdf of the track plan. […]
Read More…
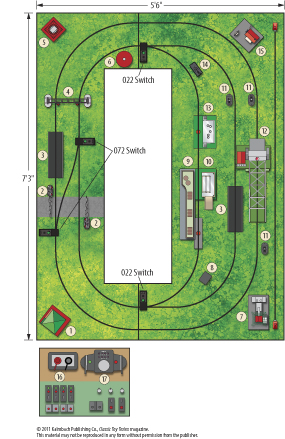
Layout designer: Paul J. Reimold Scale: O Layout size: 5 1/2 x 7 1/2 feet Track type: Lionel O Minimum curve: O-31 Originally appeared in the January 2003 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Parts list […]
Read More…
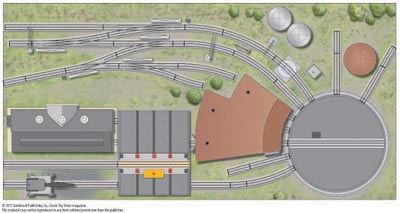
Layout designer: Kent Johnson Scale: O gauge Layout size: 4 x 8 feet Track type: Atlas O Minimum curve: O-63 Originally appeared in the March 2006 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the links below to view PDF’s related to this track plan. Track Plan Schematics Parts List […]
Read More…
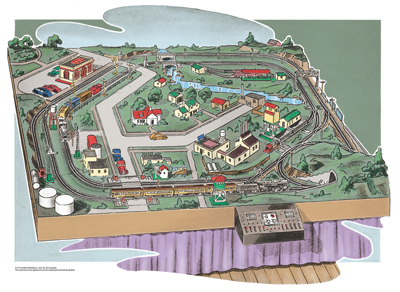
Layout designer: Neil Besougloff Scale: O Layout size: 10 x 12 feet Track type: Lionel FasTrack Minimum curve: O-36 Originally appeared in the September 2005 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Schematic Parts list […]
Read More…
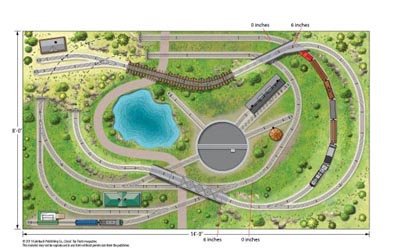
Layout designer: Neil Besougloff Scale: O Layout size: 8 x 14 feet Track type: Lionel FasTrack Minimum curve: O-48 Originally appeared in the October 2007 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Schematic Parts list […]
Read More…
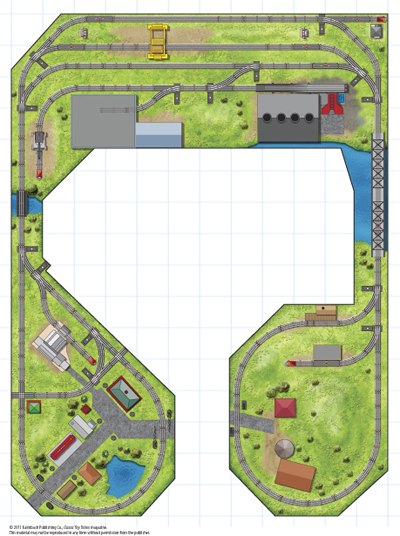
Layout designer: Dennis Waldeck Scale: O Layout size: 12 x 16 feet Track type: Lionel O Minimum curve: O-31 Originally appeared in the October 2004 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Parts list […]
Read More…

Layout designer: Anthony DiLapi Scale: O Layout size: 6 x 12 feet Track type: Lionel O gauge tubular Minimum curve: O-31 Originally appeared in the November 2004 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Art work Parts list […]
Read More…
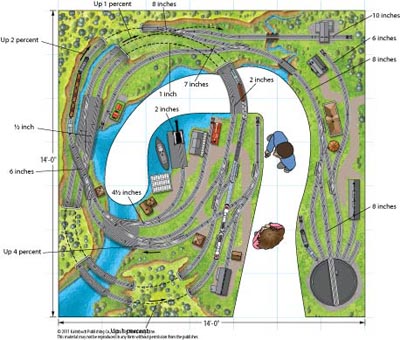
Layout designer: E. A. Engebretson and Kent Johnson Scale: O Layout size: 14 x 14 feet Track type: Atlas O Minimum curve: O-36 Originally appeared in the November 2006 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Schematic Parts list […]
Read More…
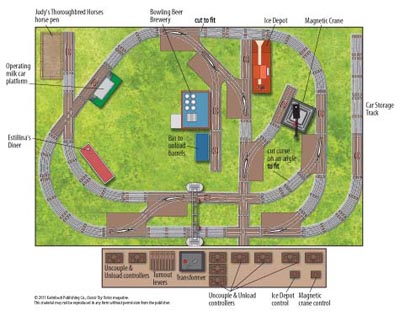
Layout designer: Dick Wise Scale: O Layout size: 4 x 6 feet Track type: Lionel sectional track Minimum curve: O-27 Originally appeared in the July 2002 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Track plan Parts list Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. […]
Read More…
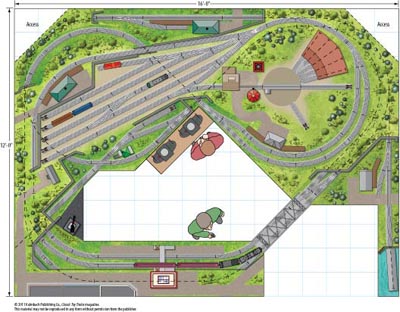
Layout designer: David Deinard Scale: O Layout size: 12 x 16 feet Track type: Atlas O Minimum curve: O-63 Originally appeared in the September 2008 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Schematic Parts list […]
Read More…












