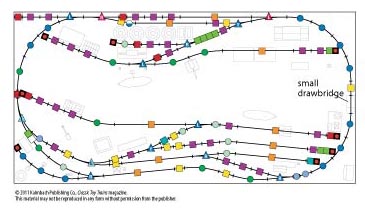
Layout designer: E. A. Engebretson and Kent Johnson Scale: O Layout size: 8 x 16 feet Track type: Atlas O Minimum curve: O-72 Originally appeared in the January 2006 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Waterfront Terminal Railroad track plan Waterfront Terminal Railroad schematic Waterfront Terminal Railroad components […]
Read More…
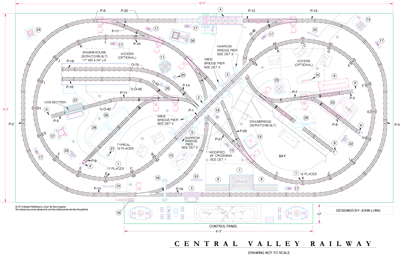
Layout designer: John Long Scale: O Layout size: 8 x 16 feet Track type: Lionel O Minimum curve: O-31 Originally appeared in the March 2004 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Wide curve track plan Wide curve track plan components […]
Read More…
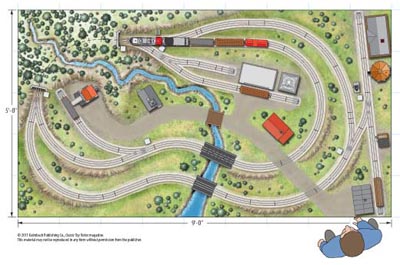
Layout designer: Kent Johnson Scale: O Layout size: 5 x 9 feet Track type: Lionel FasTrack Minimum curve: O-36 Originally appeared in the October 2006 issue of Classic Toy Trains. Click on the link to download a PDF of this track plan. Track plan Schematic Parts list […]
Read More…
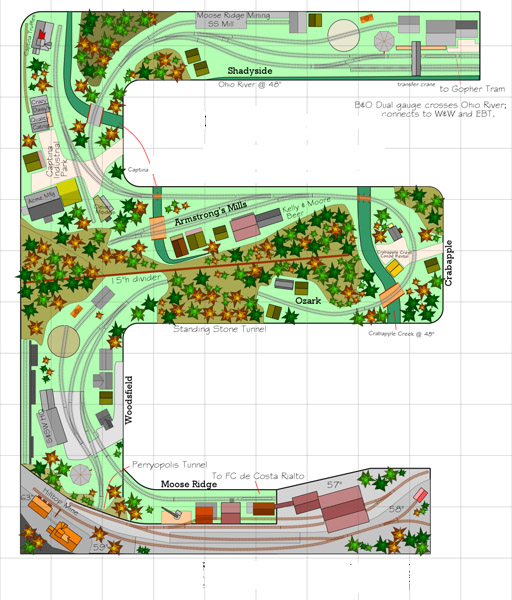
AnyRail Track Planning Software (screen shot) In designing my current layout, I wanted to move away from hand drawing track plans with all the attendant problems involved with making changes, edits, etc. I looked at several track-planning software products but found them too complicated for my needs and level of skill. Much like my attitude […]
Read More…

Read how John Armstrong developed the Southern Pacific Lines Shasta Division for Otis McGree, Jr. Main line through the mountains […]
Read More…

A house, a car, and a layout all have something in common: they turn out better when they’re built on a solid framework. This is especially true of a helix. A helix – a spiral ramp meant to lift a model train from one level of a layout to another – may not be prototypical, […]
Read More…
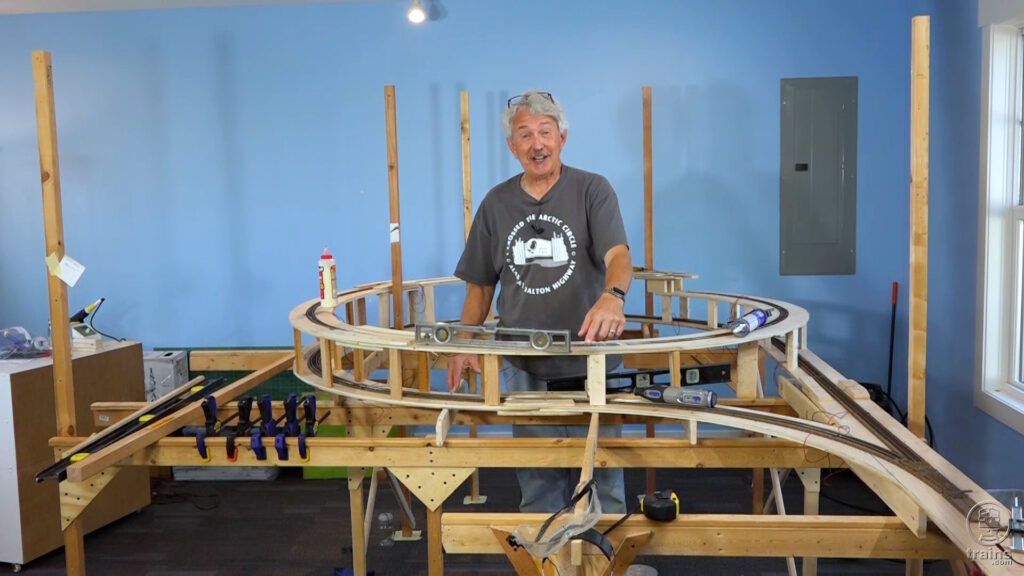

Even with a little help from a friend, host Gerry Leone still struggles with benchwork construction. But after setting joists straight and level, he jumps right into raising the grade along the helix. Discover a few new track tips and tricks along the way. […]
Read More…
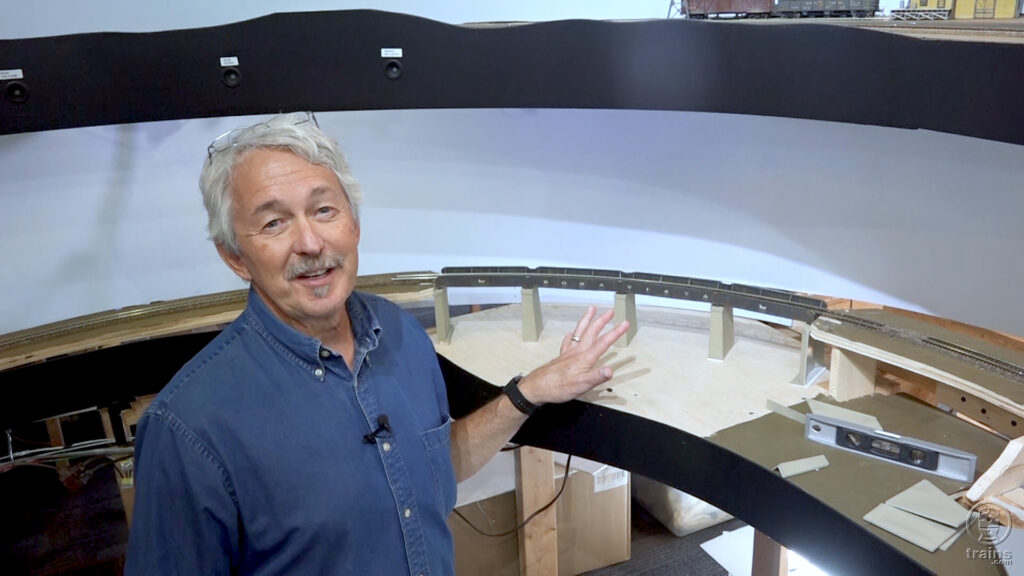

By popular demand! Back on Track host Gerry Leone jumps ahead in time to begin an effort to shape a common layout space into a unique place! In this episode, you’ll see the start of the lake scene takes the curved mainline into consideration. First, Gerry works to build up a plate girder bridge to […]
Read More…

Open-grid benchworkStarter layouts are often flat and built on a 4 x 8 sheet of plywood. However, the majority of layouts have tracks at varying heights separated by grades. The easiest way to add elevation to a layout is to use open-grid benchwork. For this type of construction you place a plywood subroadbed under the […]
Read More…

Code of railPrototype railroads use rail of varying heights and weights depending on the type and frequency of trains that run on it. On model railroads, code is the height of the rail measured in hundredths of an inch. See fig. 2. FlextrackWhile some modelers handlay their tracks by spiking the rail to individual wood […]
Read More…
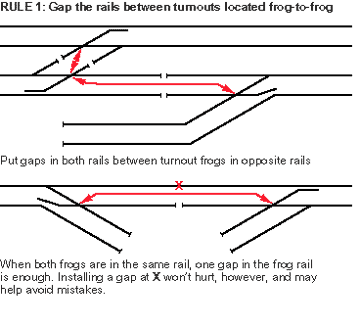
How to wire power-routing turnouts: While it may initially seem difficult, basic two-rail wiring for power-routing turnouts is easy if you understand and apply just two simple rules. The diagrams below demonstrate these crucial wiring principles. Rule 1: Gap the rails between turnouts located frog-to-frog. Place gaps in both rails, between turnout frogs in opposite […]
Read More…
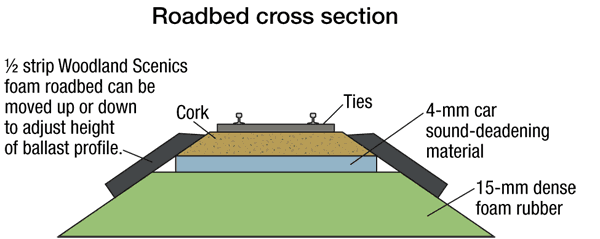
A number of years ago I started to experiment with substitutes for white glue to hold down the track and fix the ballast in an attempt to limit the transmission of sound through the benchwork. Part of my solution came in the form of acrylic-latex caulk (the type used around doors and windows). I use […]
Read More…












