
The Pennsylvania Railroad built 90 G5s class 4-6-0s between 1923 and 1925. Ten-Wheeler No. 1963 was photographed pulling away from the coaling dock at Fort Wayne, Ind., with a westbound passenger train in October 1947. J. R. Crosby The first Ten-Wheelers appeared in the late 1840s. They grew out of the need for a locomotive […]
Read More…

Santa Fe owned the largest fleet of Atlantics, and kept a handful in service until 1953. No. 1468, a 1909 Baldwin, was pinch-hitting for an ailing gas-electric car when it pulled up to the depot at Riverside, Calif., with a westbound train on January 14, 1941. Jack Whitmeyer In the 1890s there was a general […]
Read More…

C&NW subsidiary Chicago, St. Paul, Minneapolis & Omaha owned the world’s heaviest and most powerful Pacifics. No. 602 – one of the road’s three giant 4-6-2s, built by Alco in 1930 – blasts through St. Paul, Minn., with train 514 on July 5, 1953. W. H. N. Rossiter The 4-6-2, or Pacific type, grew out […]
Read More…

Henry Dreyfus created the timeless design worn by the streamlined 4-6-4s that pulled the Twentieth Century Limited. New York Central rostered North America’s largest fleet of Hudsons. In this photo, one of the speedsters prepares to depart LaSalle St. Station in Chicago. W.C. Merle, II In the early 1920s, as passenger train lengths grew and […]
Read More…

BY Neil Carlson The development of the 4-8-2 grew out of the need for a locomotive with greater power than the Pacific to handle heavy passenger trains in mountainous terrain. The first 4-8-2 in North America was built at Alco’s Richmond plant and delivered to the Chesapeake & Ohio in 1911. Chessie wanted an engine […]
Read More…

Northern Pacific 4-8-4 No. 2662 storms up the 1.8 percent grade at Muir, Mont., in 1947. Warren R. McGee With the general speed-up of passenger train schedules in the 1920s, the need arose for a more powerful version of the 4-8-2. Although it had adequate adhesion, the 4-8-2 lacked the raw horsepower to accelerate a […]
Read More…

Rayonier was one of several logging companies that operated articulated 2-6-6-2 locomotives. No. 120, an oil-burning 2-6-6-2 built in 1936, hauls a trainload of freshly cut lumber near Humptulips, Wash., on September 28, 1960. Philip C. Johnson collection In the 1890s, the Gotthard Railway in Switzerland operated the first Mallet locomotives. They were compound articulated […]
Read More…

Better than most railroads, perhaps, the Union Pacific understood fast freight service. With an expansive network of lines spread across the western states, the railroad had to maintain fast schedules in order to remain competitive. Mindful of this, UP purchased the first heavy fast freight locomotives: unique three-cylinder 4-12-2s, built by Alco from 1926 to […]
Read More…

The proving ground for Union Pacific’s locomotives was a 75-mile portion of its busy main line between Ogden, Utah, and Evanston, Wyo. Eastward trains faced a climb through the Wasatch Mountains on grades of 1 percent or better. It was an expensive line to operate, particularly given UP’s practice of running big trains that typically […]
Read More…

Sample page from Field Guide to Modern Diesel Locomotives. Sample page from Field Guide to Modern Diesel Locomotives. Greg McDonnell’s Field Guide to Modern Diesel Locomotives, from the publishers of TRAINS Magazine, picks up where Louis Marre’s Diesel Locomotives: The First 50 Years (Kalmbach 1995) leaves off. McDonnell includes histories and spotting features of Electro-Motive […]
Read More…
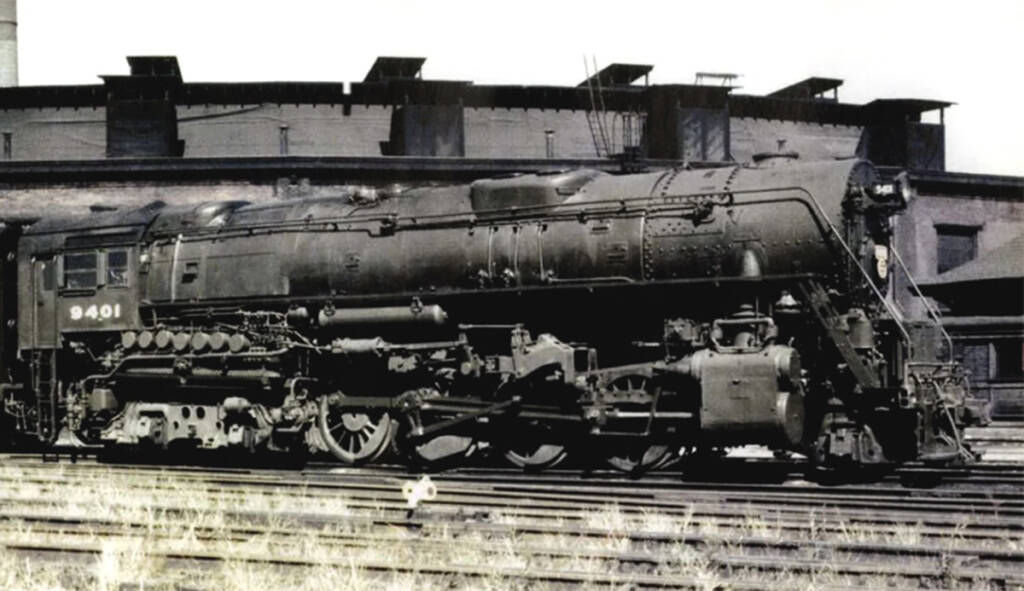
In 1920, when American railroads emerged from 26 months of government control, the prevailing philosophy of freight-train operation was to hang as many cars as possible behind a locomotive and send it out to drag its way along the line. Three locomotive types were ideal for drag freight: 2-10-2, 2-6-6-2, and 2-8-8-2. The 2-10-2 and […]
Read More…
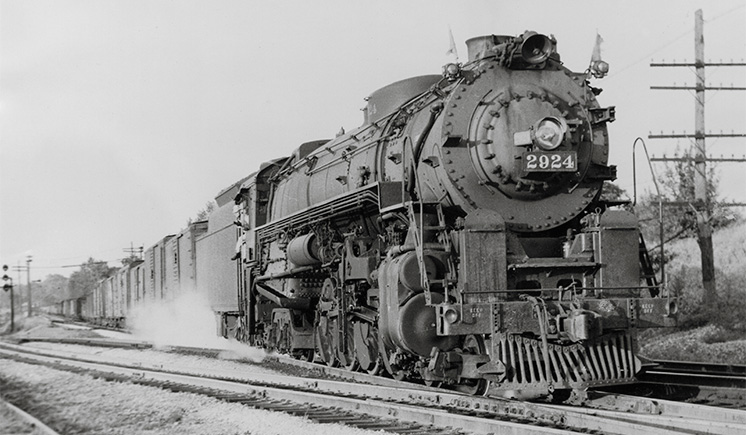

The Wabash Railway of 1900 was part of the empire that George Gould inherited from his father Jay. Its lines linked Detroit, Toledo, Chicago, St. Louis, Kansas City, Omaha, and Des Moines, and formed major hubs at Decatur, Ill., and Moberly, Mo. It had just received trackage rights on the rails of the Grand Trunk […]
Read More…












