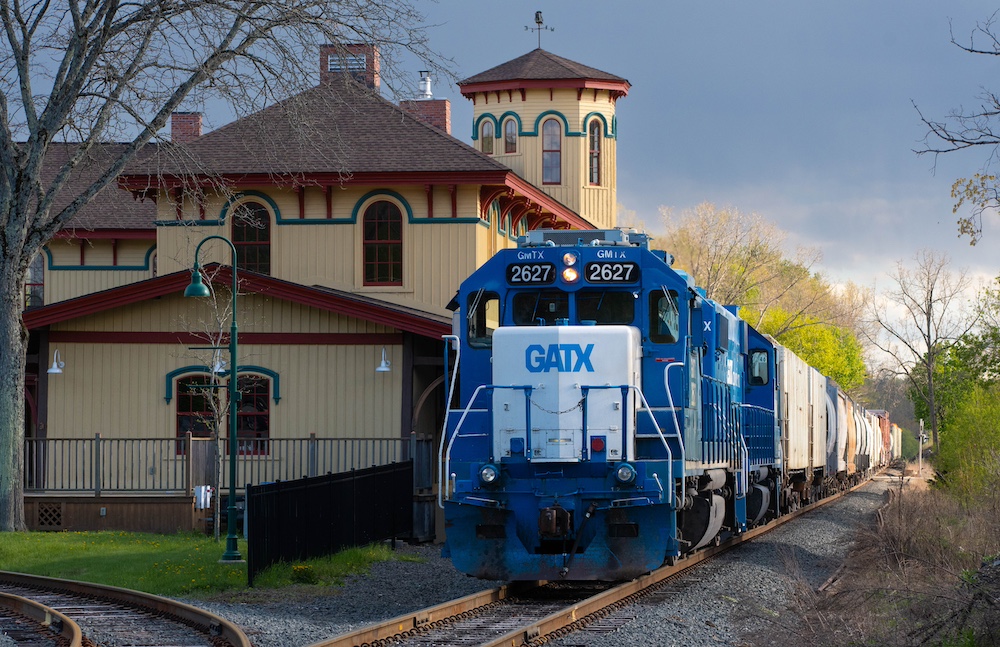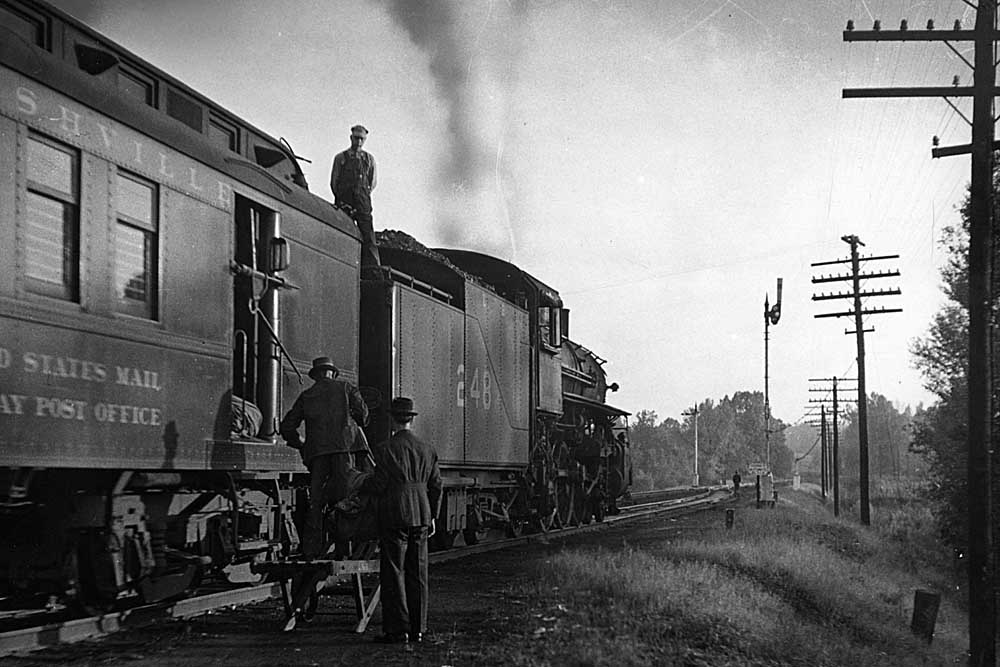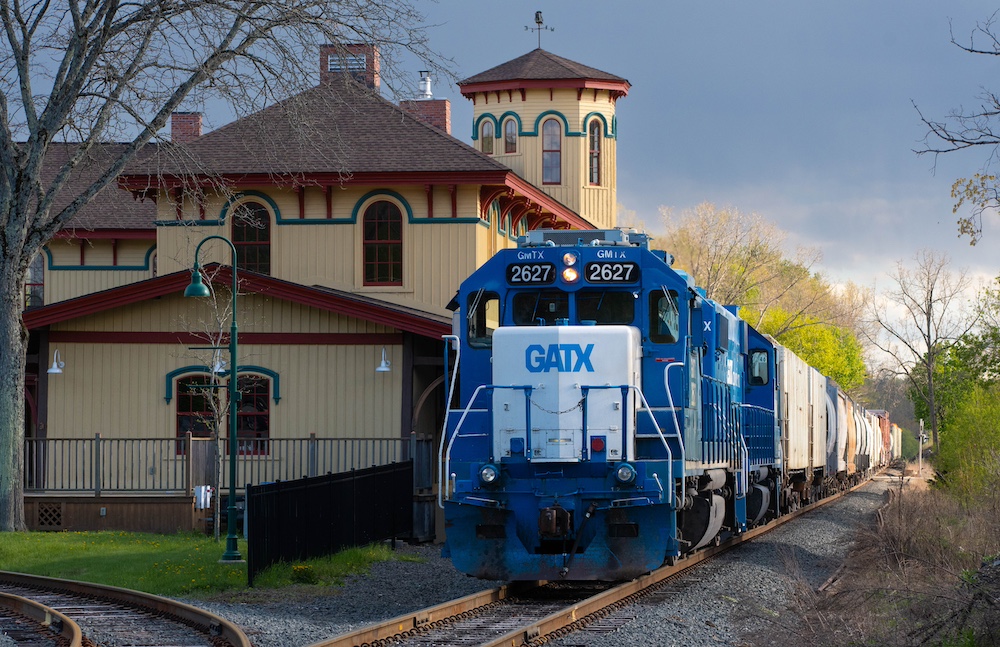
Canaan Union Depot The past The story of this historic building traces back to the 1870s, a busy time for American railroads. Across the nation new lines were being built between cities and towns, often crossing over one another. One of these crossings happened in the small town of North Canaan. Located in the northwest […]
Read More…
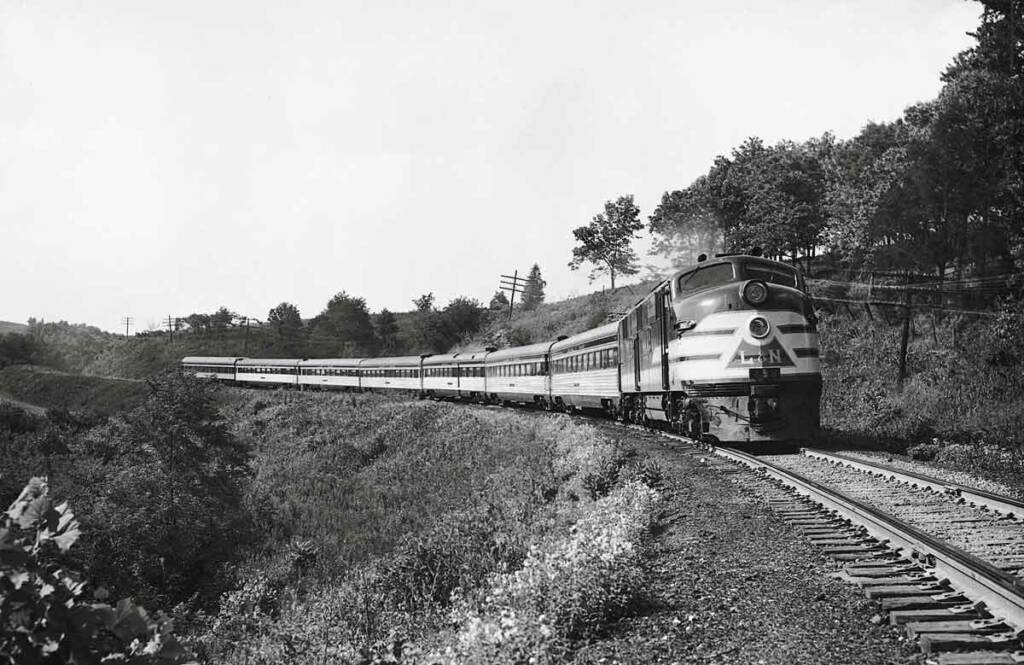

U.S. railroads introduced long-haul luxury coach trains in the 20th century to attract a more budget-conscious traveler. In the late 1930s and early 1940s, the worst of the Great Depression in the U.S. was over, and railroads began to invest in new passenger equipment; both new diesel motive power, and a radical new […]
Read More…
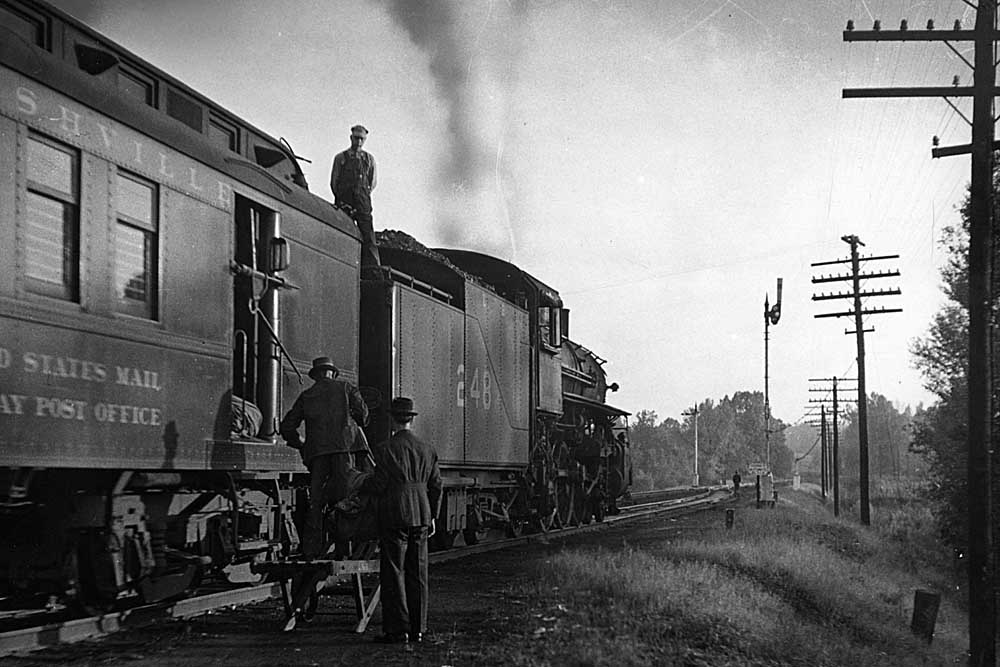
Railroad tell-tales At one time, railroad tell-tales were placed along the track on either side of low structures such as bridges and tunnels to warn crew members on top of the cars that they could not remain in a standing position while passing under the structure. Before the adoption of the air brake, and for […]
Read More…
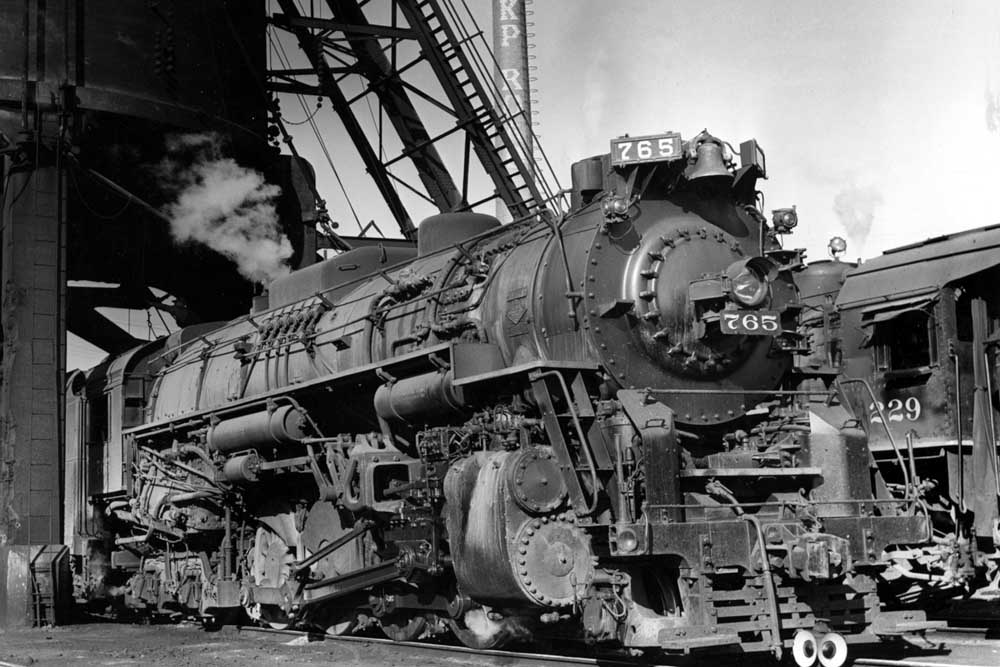

Is railroad preservation in ascendance, marked by a succession of triumphs in recent years? Or are we whistling past the wrecking ball and the acetylene torch? Is the glass half full, or half empty? The stars of a new podcast might answer “both.” Launched a few weeks ago with the title “Ahead of the Torch” […]
Read More…
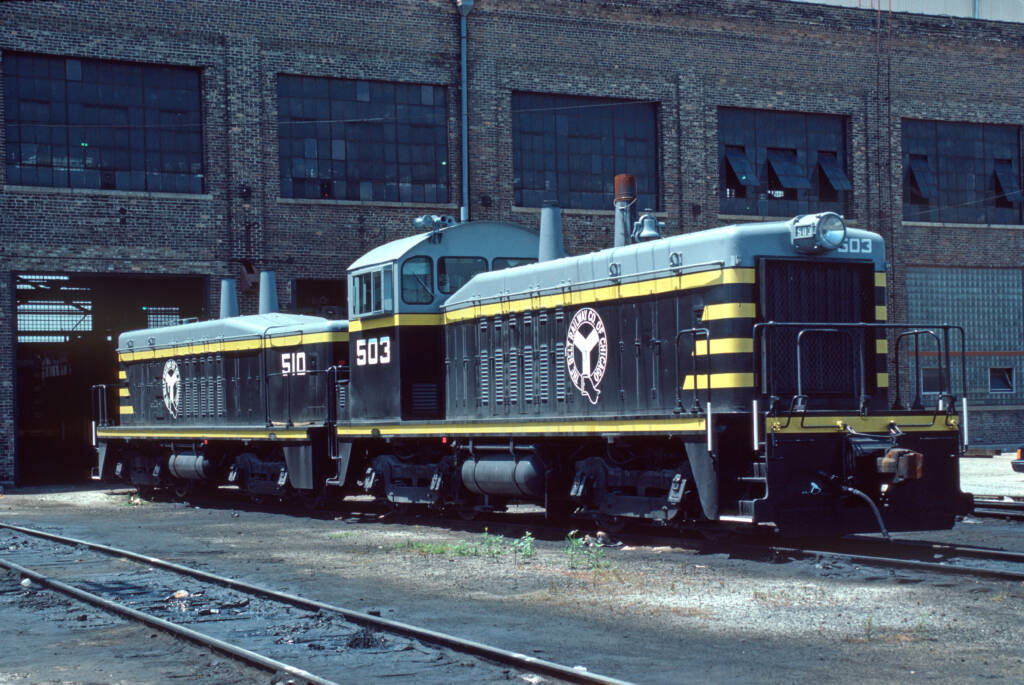

Transfer locomotives Transfer runs are trains that move cars from one freight yard usually to a nearby yard of another railroad (but not always). Early in dieselization, three of the major builders marketed locomotives built specifically for such service, called transfer locomotives, which demanded a lot of pulling power but not much speed. Transfer units […]
Read More…

What was your first byline in Trains? Steve Smedley: My first byline in Trains was “Confessions of a ‘Sacred Central Illinois’ railfan,” published in the July 2000 issue. By far the most enjoyable article I have produced. Since I worked second shift at The Pantagraph newspaper based in Bloomington, Ill., and prior to that at […]
Read More…
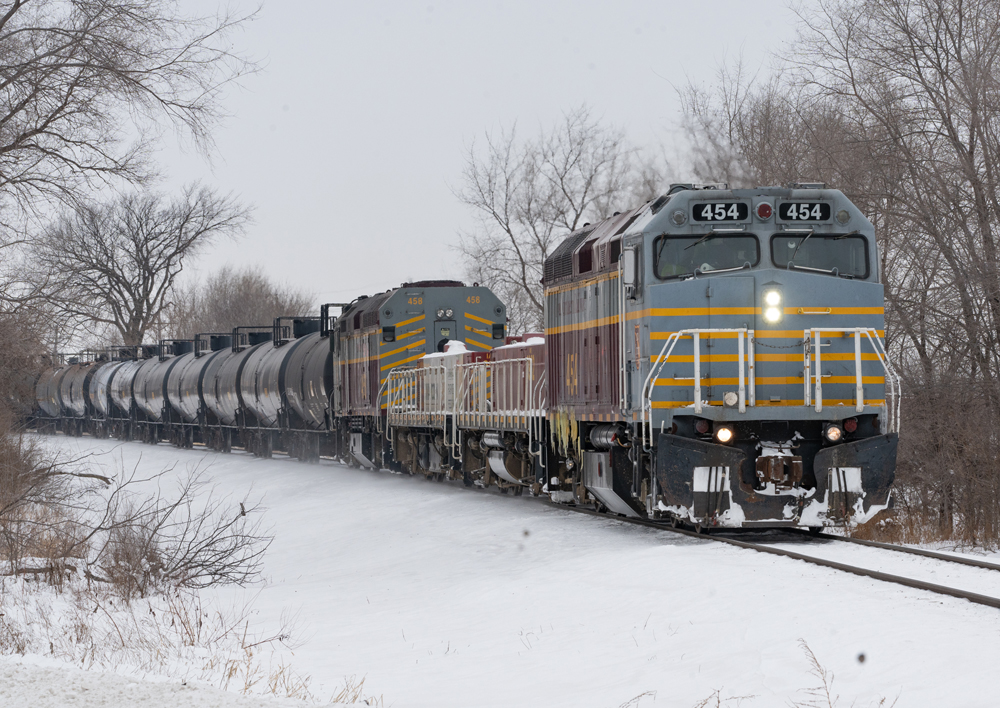

F40M-2F locomotives In the late 1990s, Amtrak converted a handful of its F40PH locomotives to locomotives suitable for freight service. At the time, new Genesis engines from General Electric were fast replacing its massive fleet of F40PHs in mainline service. Amtrak would produce 14 F40M-2F locomotive that featured a number of changes, including removal of […]
Read More…
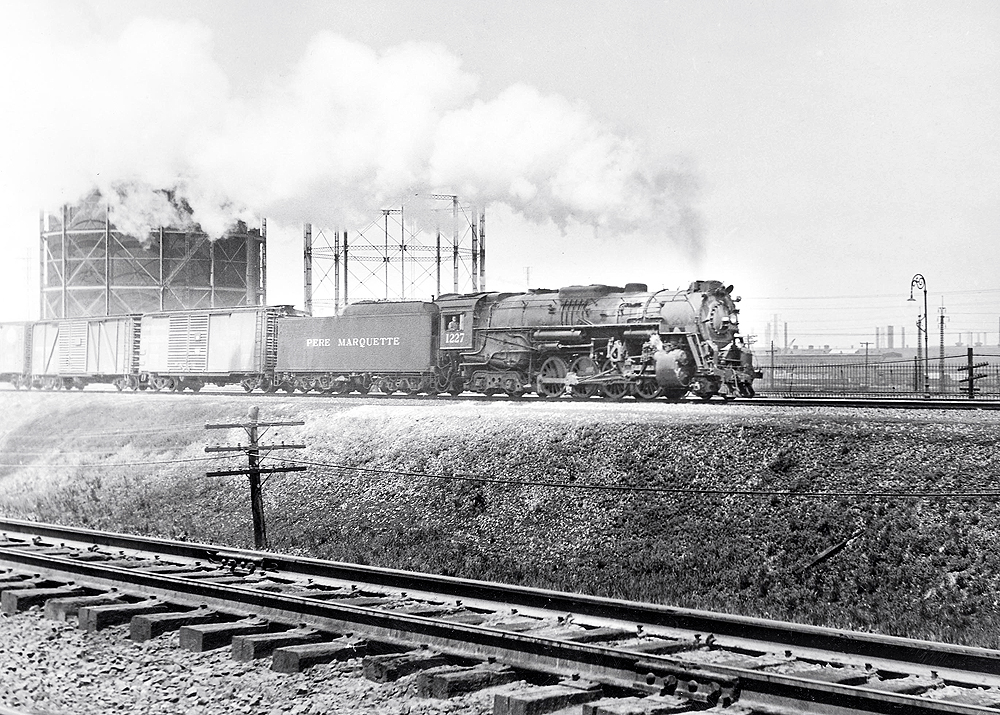

By the late 1930s, the Pere Marquette Railway had made a big splash in motive power acquisition. And rightly so, as the tired and second-rate fleet of steam locomotives was not enough to pull the Michigan railroad out of the hardship of the Great Depression. An order of 15 N-class 2-8-4s initially was rolled […]
Read More…
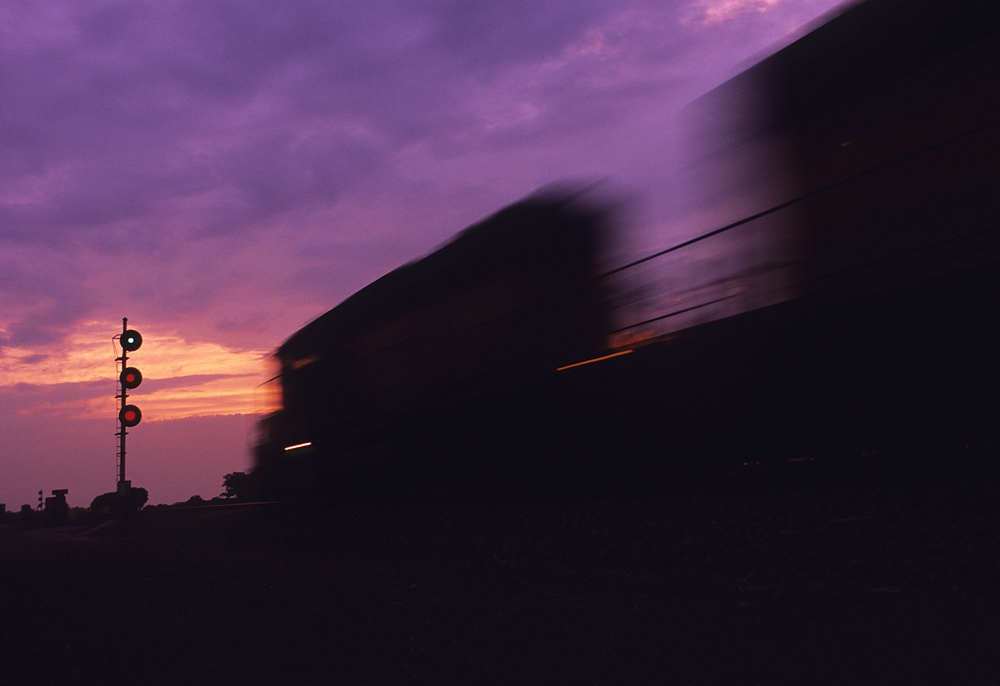

Train signals All dark, two silent sentinels guard their respective tracks on the double-track main line. Just beyond them is a crossover enabling trains to switch from one track to another. Beyond the crossover, a similar set of signals faces the opposite way. Suddenly, the dark signals light up, each displaying three columns of red […]
Read More…
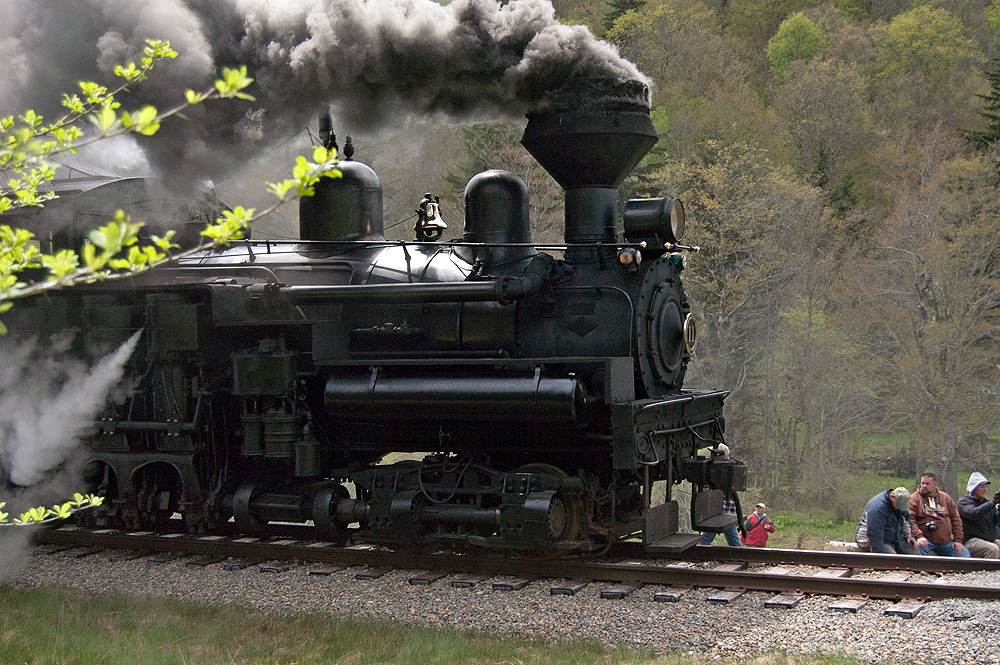

Railfanning with kids can be the most rewarding and/or the most frustrating experience. Regardless of a child’s interests or capabilities, the amount of enjoyment adults and children get out of watching trains together depends primarily on the adults in charge. If you don’t already have your own style and methods for taking kids to watch […]
Read More…
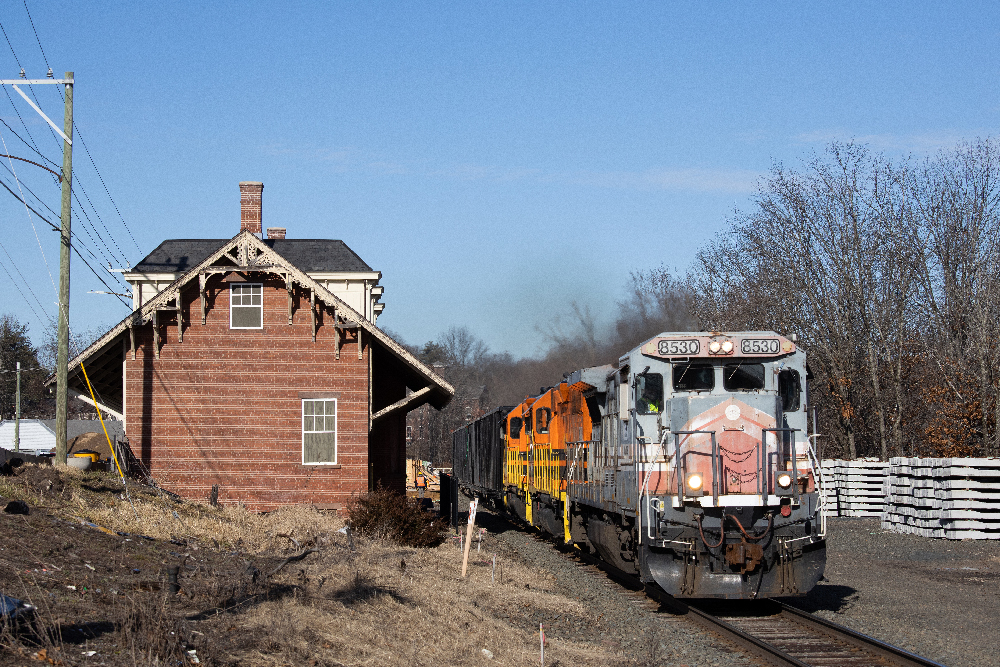

Connecticut Southern Railroad was created by short line holding company RailTex in 1996, assuming Conrail’s freight operations over 55 miles of Amtrak’s Springfield Line between Springfield, Mass., and North Haven, Conn., as well as branches the new railroad purchased from Conrail. Four years later, RailTex was purchased by RailAmerica, which in turn was acquired by […]
Read More…
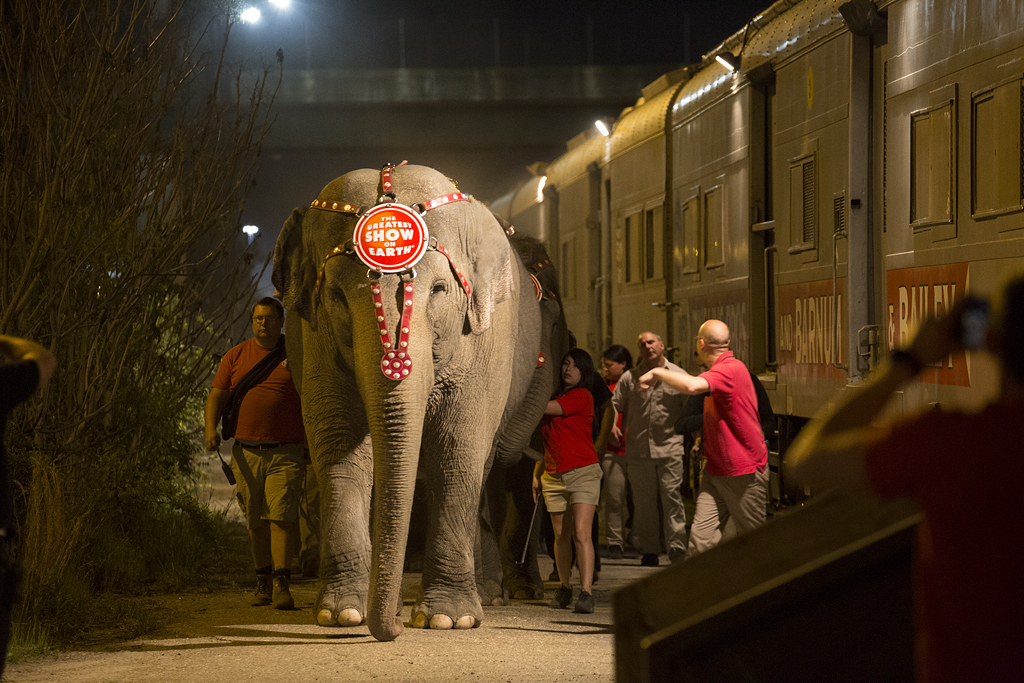

Great Circus Train In January 2017, the Ringling Bros. Barnum & Bailey circus announced it was closing down after more than 100 years in operation. For many, the transportation of the “Greatest Show on Earth” — its performers, animals and equipment — has been just as fascinating as the show itself. Circus trains became an […]
Read More…