
WASHINGTON — Travelers who wish to take small dogs or cats in carry-on cases with them aboard Amtrak trains are getting more choices starting Feb. 16, when they will be welcomed on long-distance train coaches for trips up to seven hours. The following Saturday, a pilot program scheduled through June 12 will begin on weekend […]
Read More…

Visit Norfolk Southern’s fabulous Fostoria District, connecting Fort Wayne, Ind., and Bellevue, Ohio! See fast freights, now-historic Triple Crown RoadRailer trains, and even Nickel Plate Road No. 765! Bought to you by Trains Magazine! Watch more: Trains Presents: NS Fostoria District, Vol. 2 Trains Presents: NS Fostoria District, Vol. 3 Trains Presents: Winter at the […]
Read More…

Assistant Editor Brian Schmidt talks with John Gruber about the history of the famed Chicago North Shore & Milwaukee interurban and a related art exhibit at the Milwaukee School of Engineering’s Grohmann Museum. Gruber is a co-founder of the Center for Railroad Photography & Art, based in Madison, Wis., and a curator of the exhibition […]
Read More…

Streamliners: Locomotives and Trains in the Age of Speed and Style By Brian Solomon Voyageur Press, 400 First Avenue North, Suite 400 Minneapolis, MN 55401; 208 pages, 115 color & 81 b/w photos; hardcover, 8.5 x 11 inches; $35 www.quartoknows.com Railroading in the U.S. saw rapid change between the 1930s and 1950s. That is likely […]
Read More…
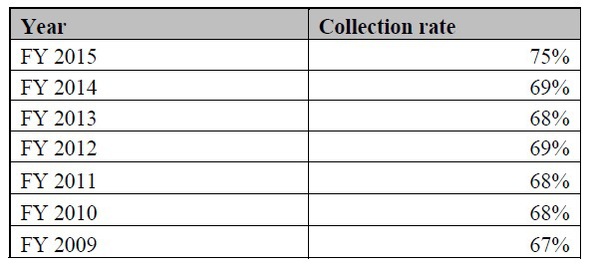
Collection rate on railroad fines (by year) Federal Railroad Administration Reasons for railroad civil fines (for fiscal year 2015) Federal Railroad Adminisrtation WASHINGTON — The Federal Railroad Administration today announced that it has stepped-up enforcement of railroad safety regulations led to the highest-ever civil penalty collection rate in the agency’s 50-year history. For fiscal year […]
Read More…

Host Drew Halverson heads to the Northwest and back across the Canadian border to begin his most ambitious railfan outing yet! Drew enlists MRVP’s Kent Johnson and pilot pal Charlie Conway to help capture railroad action in one of the most picturesque river canyons in North America. Drew and the crew also catch BNSF street […]
Read More…
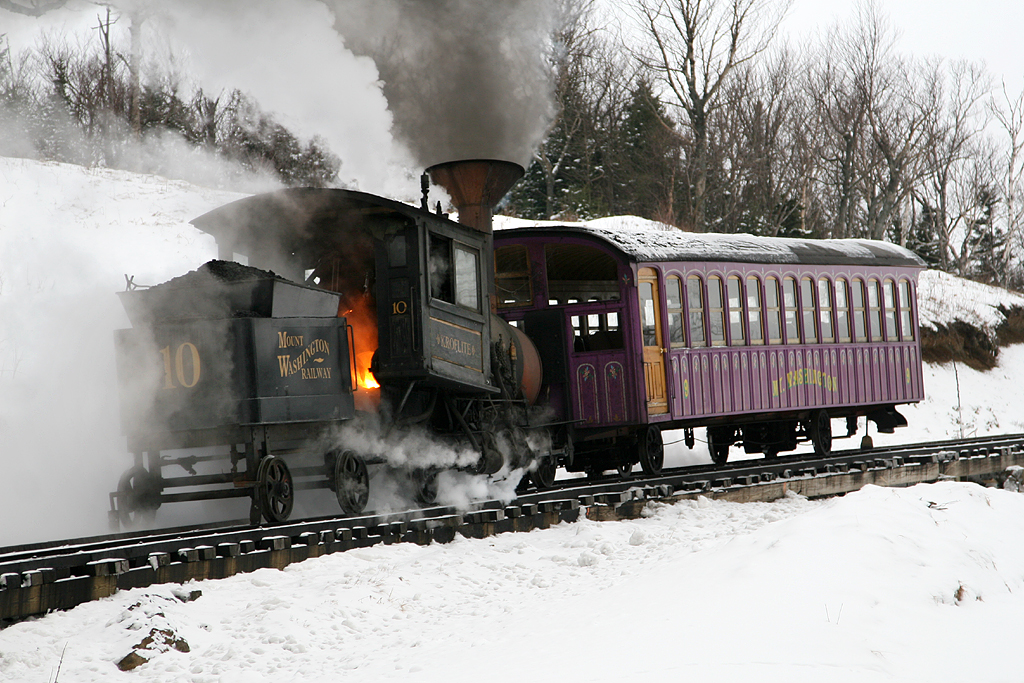

This “Trackside with Trains” photo contest result comes from January 2016. The theme was “Fire.” Trackside with Trains was a regular, periodic contest among Trains website visitors from the earlier 2000s until October 2018. Anyone in the world who wanted to participate, could, and with rare exception, have their images judged by viewers with […]
Read More…
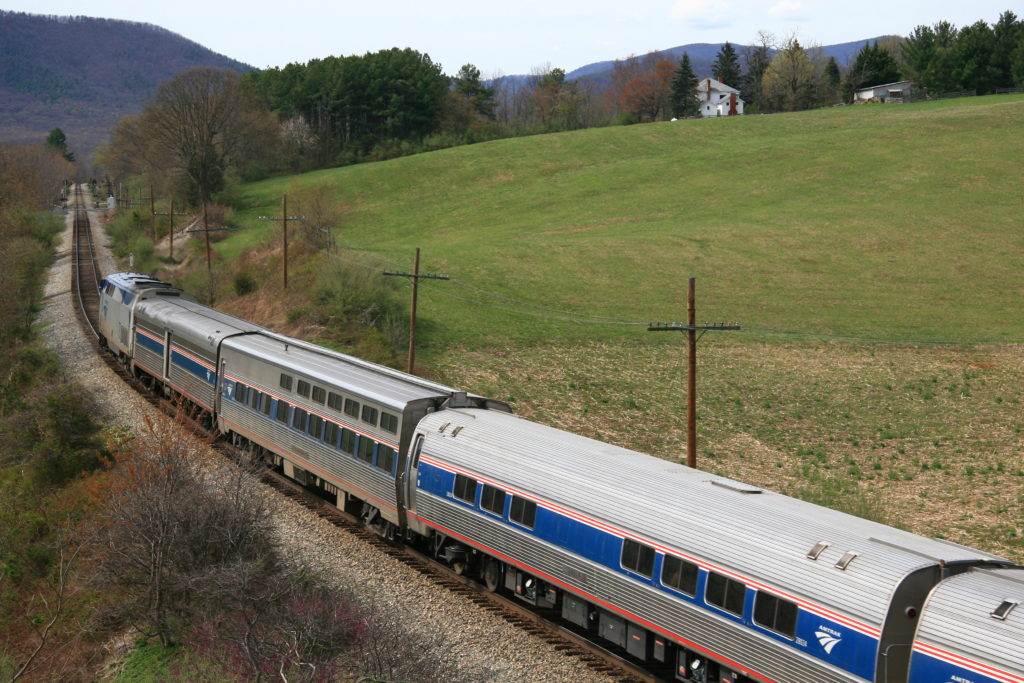

Cardinal heads west near Swoop, Va., east of Staunton, in April, 2013 Bob Johnston WASHINGTON—Starting this month, Amtrak will begin offering business class on the triweekly Chicago-Washington-New York Cardinal. The decision to do so was made recently, so it is not reflected in the new “Winter Spring 2016” timetable effective Monday, Jan. 11. The launch, […]
Read More…
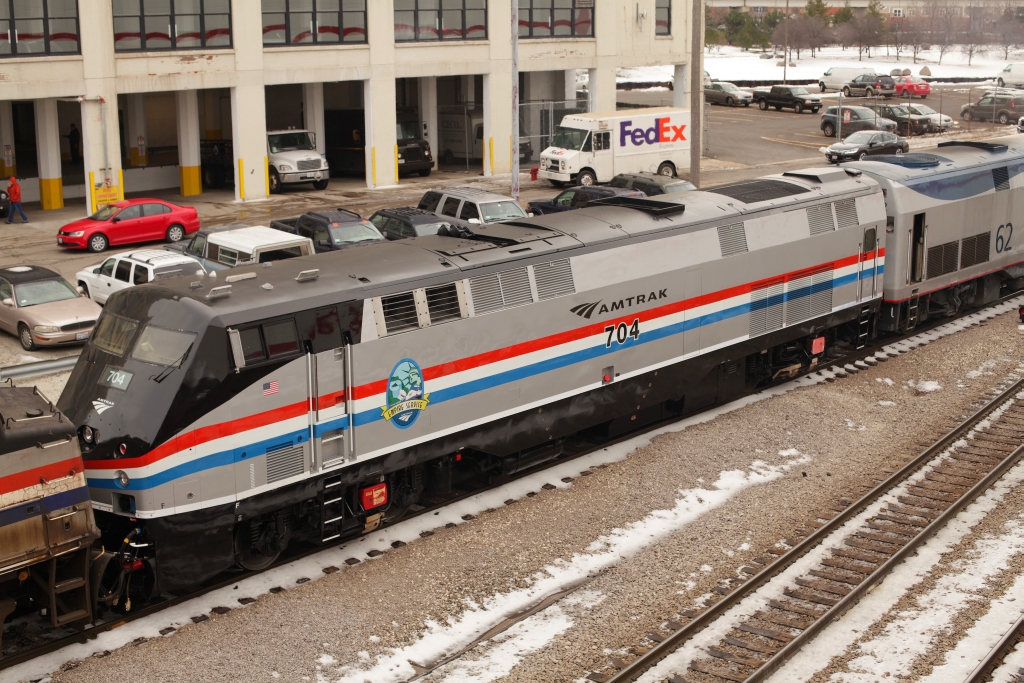

No. 704 trails on the westbound ‘Cardinal’ as it arrives in Chicago on Jan. 7. Mark Hinsdale NEW YORK – Passengers along the Empire Service route to Upstate New York can look forward to more of Amtrak’s “Phase III” paint scheme. GE P32AC-DM No. 704 rolled into the windy city last week displaying a Phase […]
Read More…
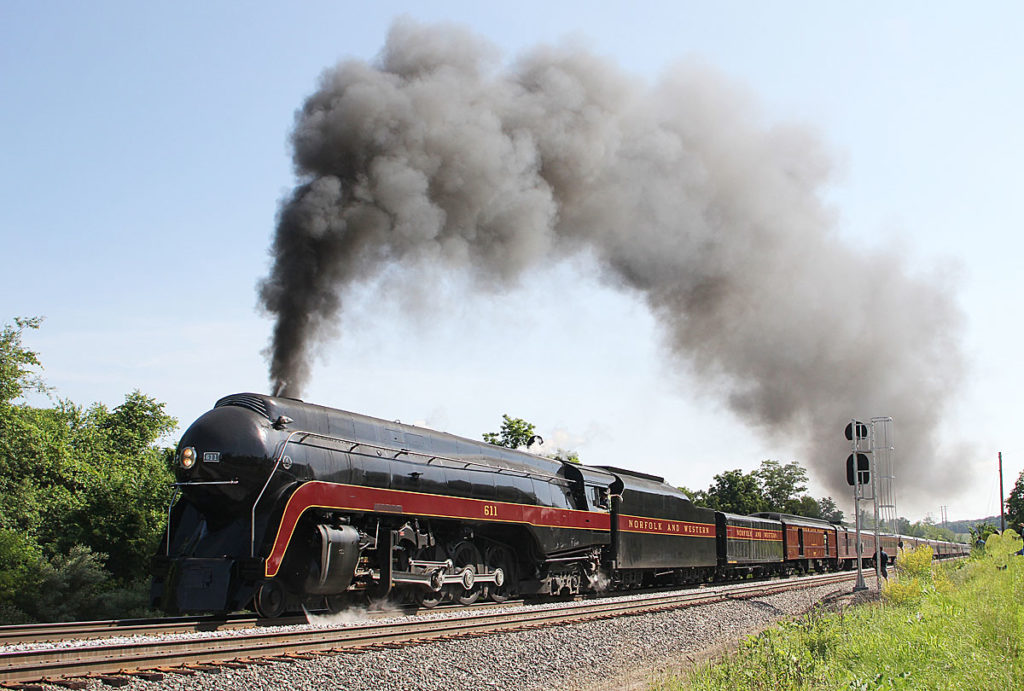

ROANOKE, Va. – World famous Norfolk & Western Class J No. 611 will pull public excursions four weekends between April and June in its home state of Virginia and North Carolina, the Virginia Museum of Transportation and North Carolina Transportation Museum announced Monday. The announcement ends weeks of speculation as to the extent of NS’s […]
Read More…










