
This February 2026 episode of Cody’s Office features an exciting product lineup, essential modeling tips, and viewer questions. Senior Editor Cody Grivno showcases the HO scale Greenbrier five-trough coil car from Rapido Trains and Athearn’s Genesis series GE Dash 9-44CW locomotive. He also reviews the new Firecrown Media book, Tales of the Rails. Cody demonstrates […]
Read More…

This February 2026 episode of Cody’s Office features an exciting product lineup, essential modeling tips, and viewer questions. Senior Editor Cody Grivno showcases the HO scale Greenbrier five-trough coil car from Rapido Trains and Athearn’s Genesis series GE Dash 9-44CW locomotive. He also reviews the new Firecrown Media book, Tales of the Rails. Cody demonstrates […]
Read More…

Q: I’m getting back into model railroading after a 50 year hiatus. I’m having trouble with knuckle couplers that won’t connect. I have new rolling stock from Athearn, Walthers, ScaleTrains, and Accurail. I also have several cars that I converted to Kadee. Couplers from different manufacturers don’t seem to work together. Are there any combinations […]
Read More…

Rapido Trains recently announced several HO scale GO Transit models to commemorate the 60th anniversary of the Toronto-area transit service in 2027. Offerings will include a General Motors Diesel Division (GMDD) GP40TC, FP7 Auxiliary Power Control Unit (APCU), and Hawker Siddeley RTC-85 single-level commuter cars, as well as boxed sets. Leading things off is the […]
Read More…

Q: I have several On30 locomotives with Digital Command Control (DCC), but was recently gifted a passenger set that has a direct-current (DC) locomotive. If some DCC locomotives are sitting on the track, can I use a DC transformer to operate the DC engine on the same track without damaging the DCC locomotives? What would […]
Read More…
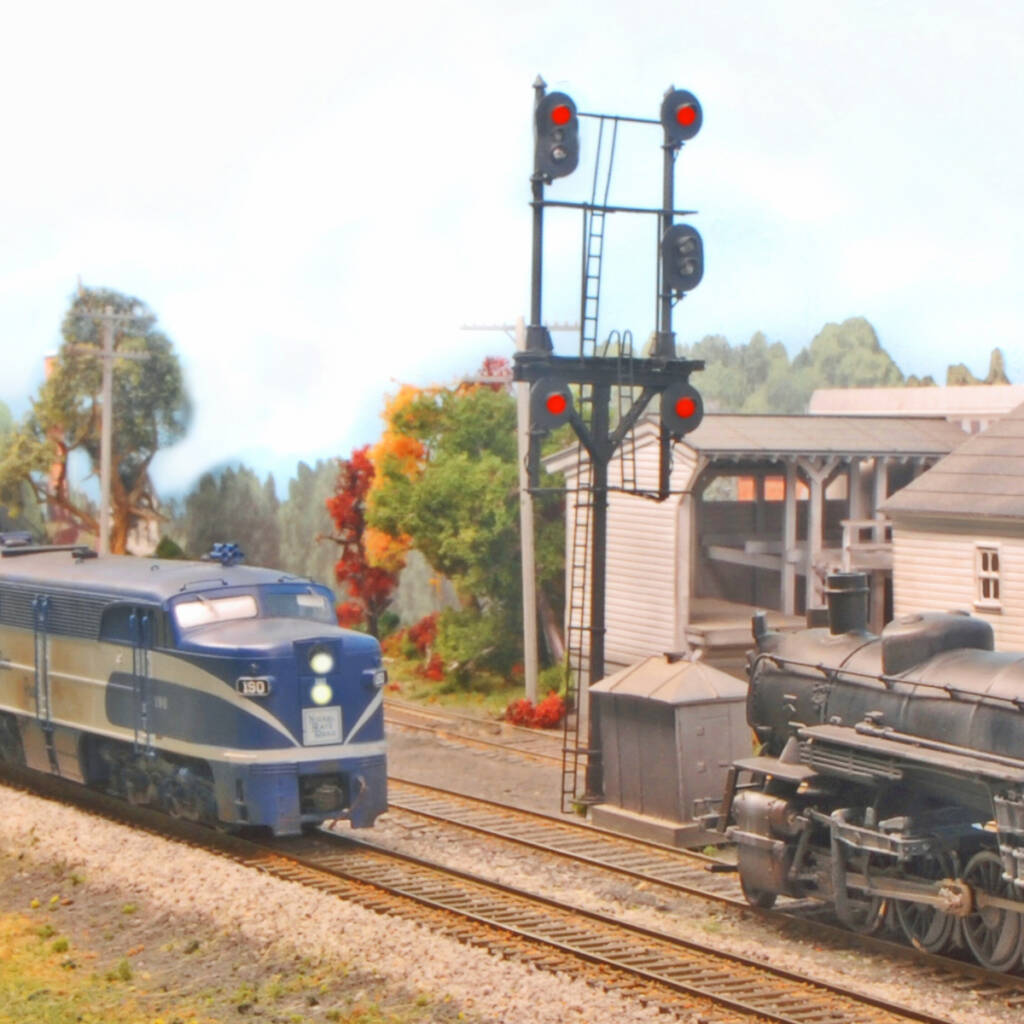

Q: The cover of the November 2025 issue of Model Railroader shows the signals for the west end of the Veedersburg, Ind., siding. The signal for entering the siding has no middle head so the best it could display is slow clear, but the signal for leaving the siding has a middle head and only […]
Read More…
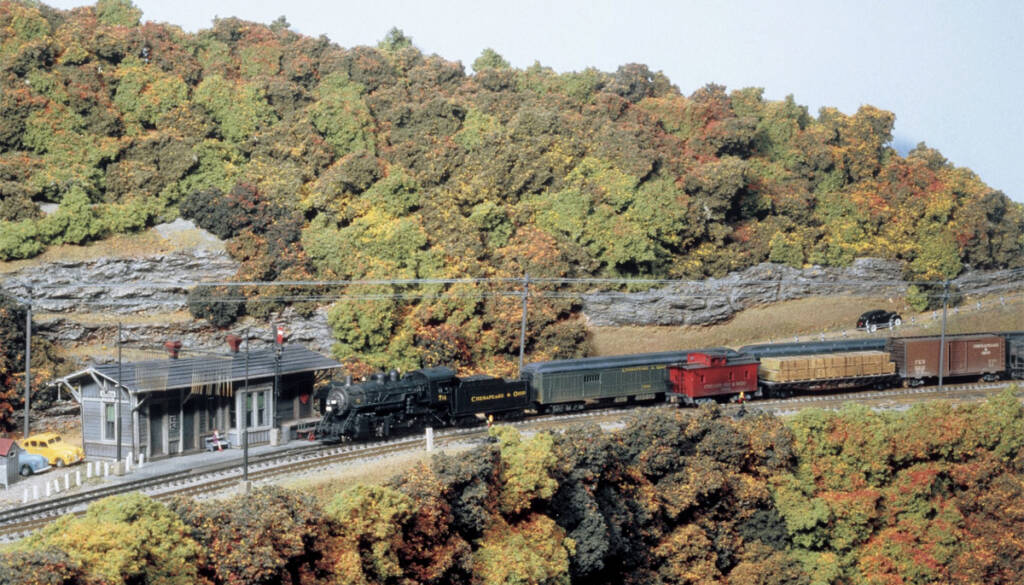

When I first started work on my layout, I built wood and plastic structure kits. I quickly grew frustrated with these buildings as few of them represented those found in Appalachia and along the Chesapeake & Ohio. Considering the lack of accurate building available on the marktet, I began scratchbuilding my own structures from wood […]
Read More…
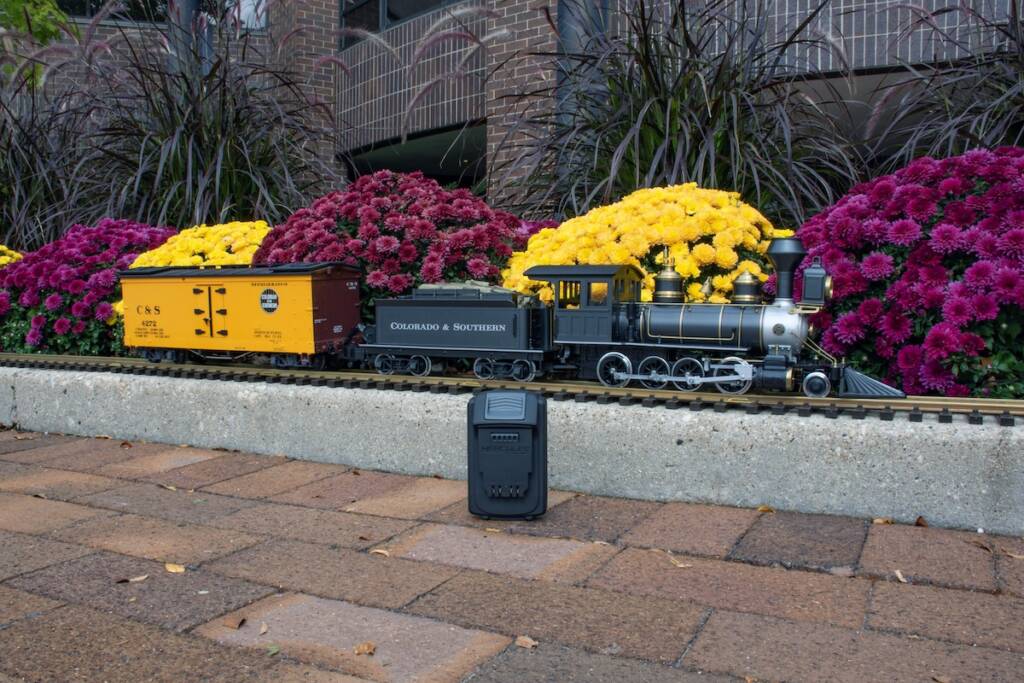

I never thought I’d get serious about Large scale (G gauge) model railroading, but here I am. This past summer, I successfully bid on a 1:22.5-scaled C-16 2-8-0 in Colorado & Southern livery at an online auction. This model, from the 1989 product line of the former Delton Locomotive Works (before its tooling went to […]
Read More…
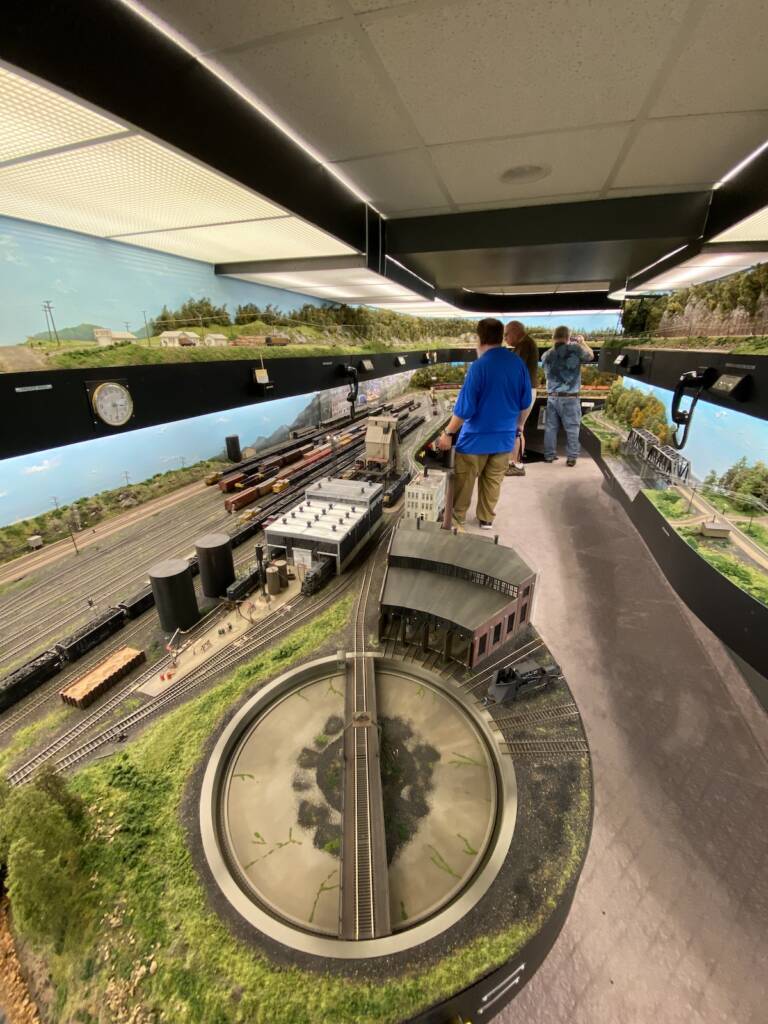

Open houses, whether at model railroad clubs or private home layouts, offer fantastic opportunities to connect with fellow modelers and share the hobby. It’s also a joy to see what makes a layout tick and how one differs from another. While hosting an open house requires careful planning — as Arlan Tietel thoroughly explains in […]
Read More…
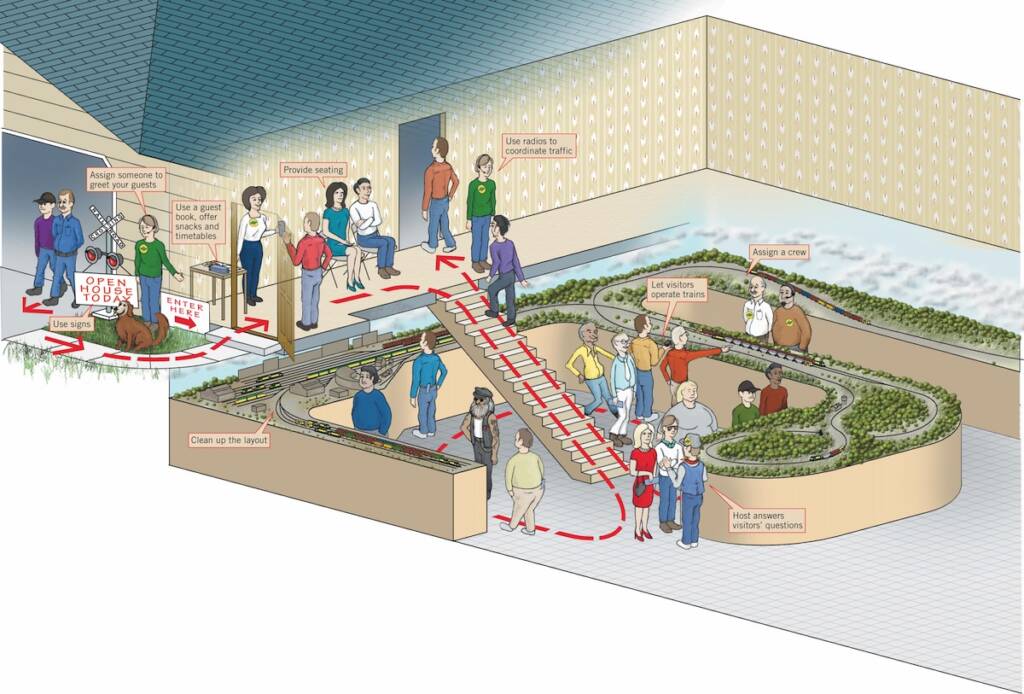
This article was originally published in the November 2002 issue of Model Railroader. Hosting an open house is a great way for model railroaders to share the hobby with others. But coordinating one that people will never forget requires not only good planning, but practice. In the past two decades, I’ve hosted several open houses, […]
Read More…
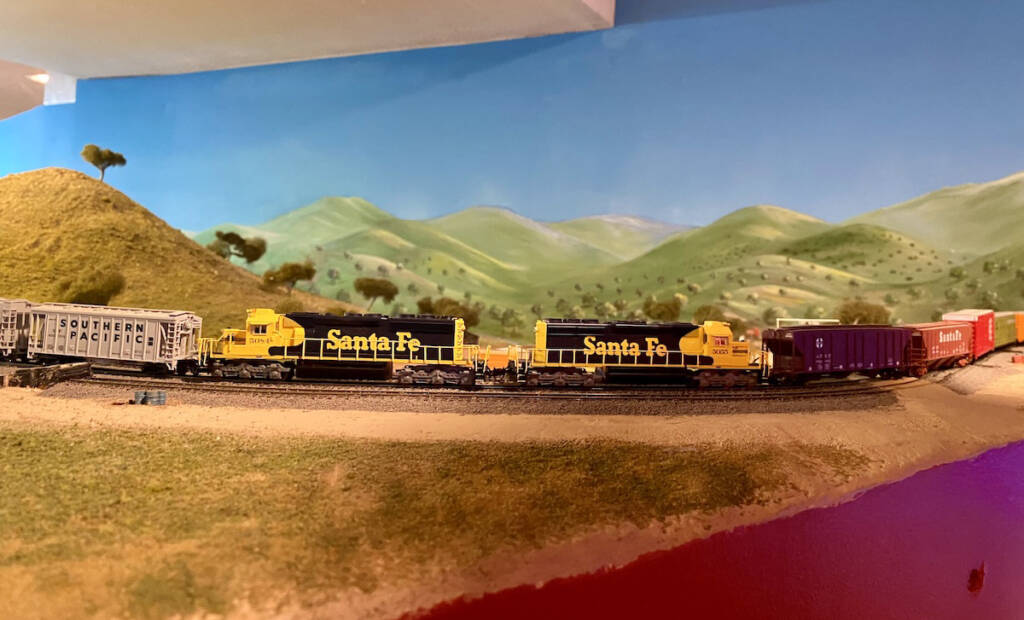

Retired Model Railroader Managing Editor Jim Kelly remains active in honing his N scale skills and craftsmanship. The result has been the fourth incarnation of his Tehachapi Pass layout. Set in 1985, both the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe and Southern Pacific traverse the 2% grade between Bakersfield and Tehachapi, Calif., with the famous Tehachapi […]
Read More…
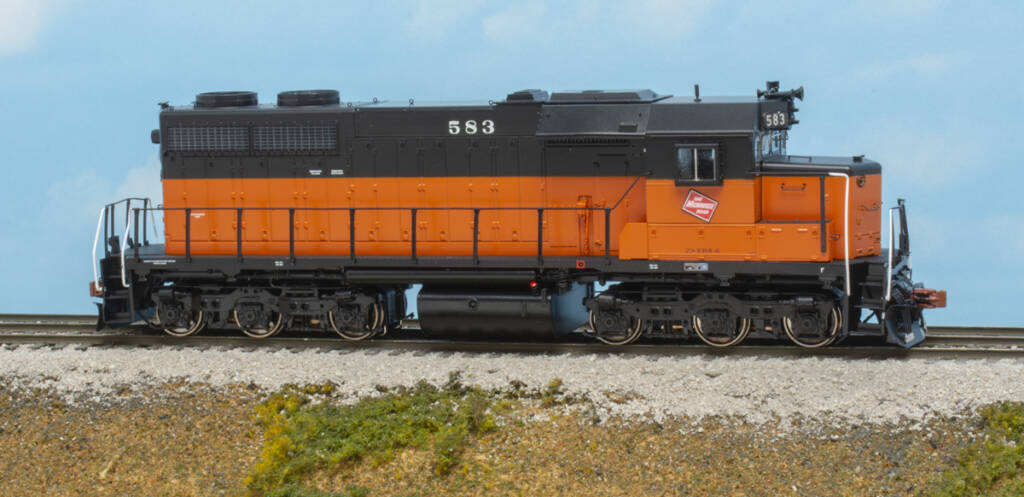

Q: In the May 2025 Ask MR, the answer to a question about early diesel power for the Milwaukee, Racine & Troy included this statement: “For road power, the MR&T would most likely turn to four-axle units, such as the Alco RS1 through RS3 and EMD GP7 and GP9. It’s possible the MR&T could have […]
Read More…











